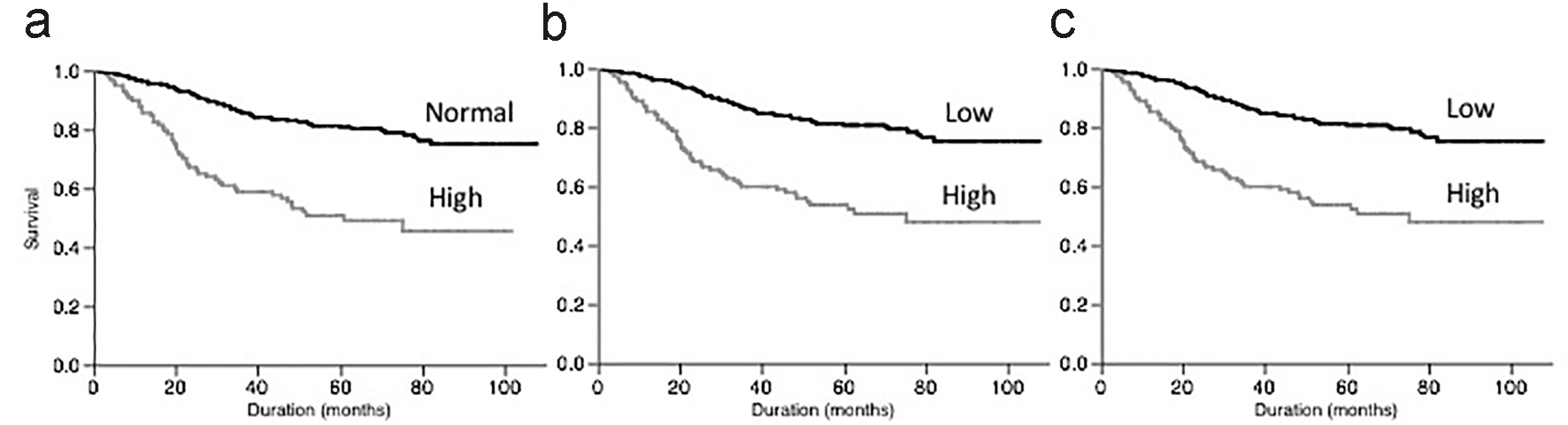
Figure 1. Survival of patients according to serum CEA concentration (a), BSA-based CEA amount (b) and HCT-based CEA amount (c).
| World Journal of Oncology, ISSN 1920-4531 print, 1920-454X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, World J Oncol and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.wjon.org |
Original Article
Volume 8, Number 2, April 2017, pages 41-44
Does Obesity-Related Hemodilution of Carcinoembryonic Antigen Exist in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients?
Figure

Tables
| Low BMI | Normal BMI | High BMI | Total | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEA: carcinoembryonic antigen; BMI: body mass index. | |||||
| Age | |||||
| ≤ 65 | 19 | 68 | 37 | 124 | 0.070 |
| > 65 | 40 | 149 | 68 | 257 | |
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 32 | 120 | 44 | 196 | 0.668 |
| Female | 27 | 97 | 61 | 185 | |
| Smoking status | |||||
| Never | 26 | 94 | 51 | 171 | 0.577 |
| Current/former | 33 | 123 | 54 | 210 | |
| Histology | |||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 42 | 161 | 91 | 294 | 0.016 |
| Others | 17 | 56 | 14 | 87 | |
| pStage | |||||
| I | 42 | 169 | 84 | 295 | 0.433 |
| II-III | 17 | 48 | 21 | 86 | |
| pT status | |||||
| pT1 | 33 | 153 | 71 | 257 | 0.114 |
| pT2-3 | 26 | 64 | 34 | 124 | |
| pN status | |||||
| pN0 | 51 | 182 | 92 | 325 | 0.645 |
| pN1-2 | 8 | 35 | 13 | 56 | |
| CEA | |||||
| Normal | 39 | 160 | 80 | 279 | 0.375 |
| High | 20 | 57 | 25 | 102 | |
| Low BMI | Normal BMI | High BMI | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. BMI: body mass index; BSA: body surface area; HCT: hematocrit; PV: plasma volume; CEA: carcinoembryonic antigen. | ||||
| BSA-based PV | 2.3 ± 0.2 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | 2.7 ± 0.3 | < 0.001 |
| HCT-based PV | 1.8 ± 0.3 | 2.3 ± 0.3 | 2.7 ± 0.4 | < 0.001 |
| Serum CEA concentration | 28.1 ± 3.7 | 12.2 ± 0.8 | 15.5 ± 1.5 | 0.171 |
| BSA-based CEA amount | 25.5 ± 64.8 | 15.1 ± 31.6 | 15.4 ± 41.8 | 0.842 |
| HCT-based CEA amount | 20.1 ± 52.5 | 13.6 ± 29.2 | 15.1 ± 41.1 | 0.598 |