Figures
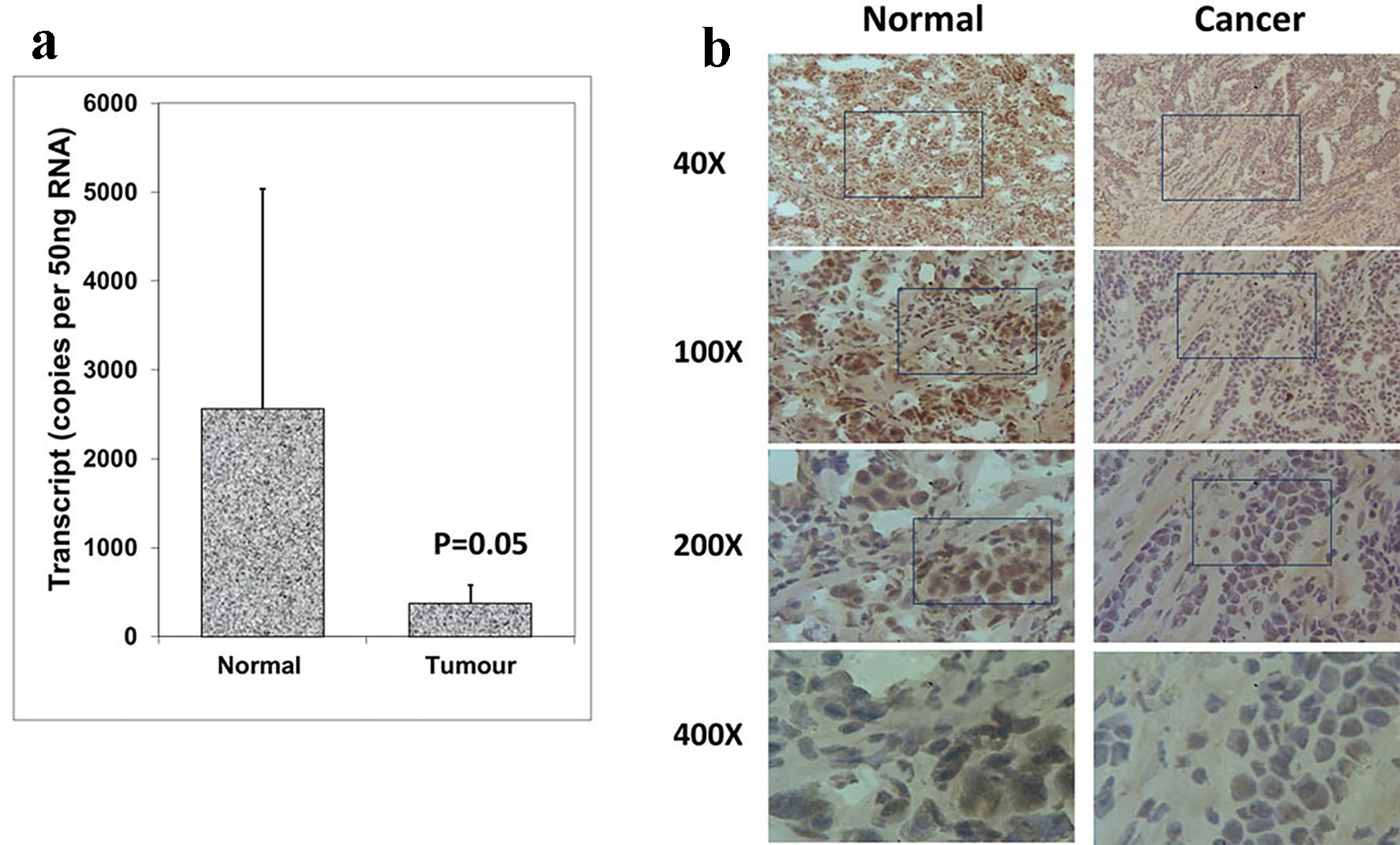
Figure 1. Expression of Aurora kinase A in breast cancer tissues. (a) Aurora kinase A transcripts level was decreased in human breast cancer. (b) Immunohistochemical staining of Aurora kinase A in normal breast tissue (left panel) and tumor tissue (right panel).
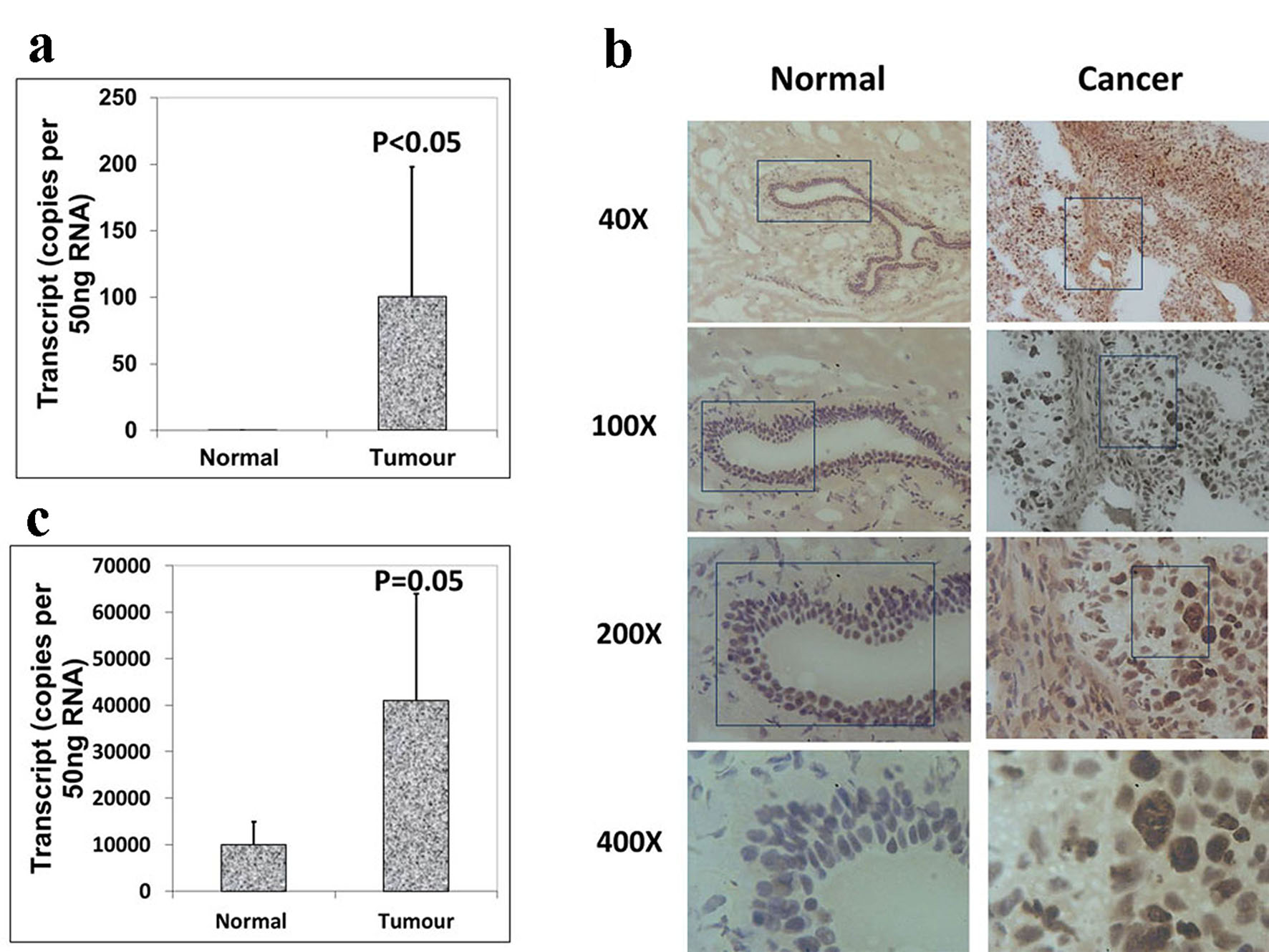
Figure 2. Expression of Aurora kinase B and C in breast cancer tissues. (a) The expression of Aurora kinase B is higher in breast cancer tissues. (b) Immunohistochemical staining of Aurora kinase B in normal background tissue (left panel) and breast tumor tissue (right panel). (c) Aurora kinase C transcripts level was increased in human breast cancer.
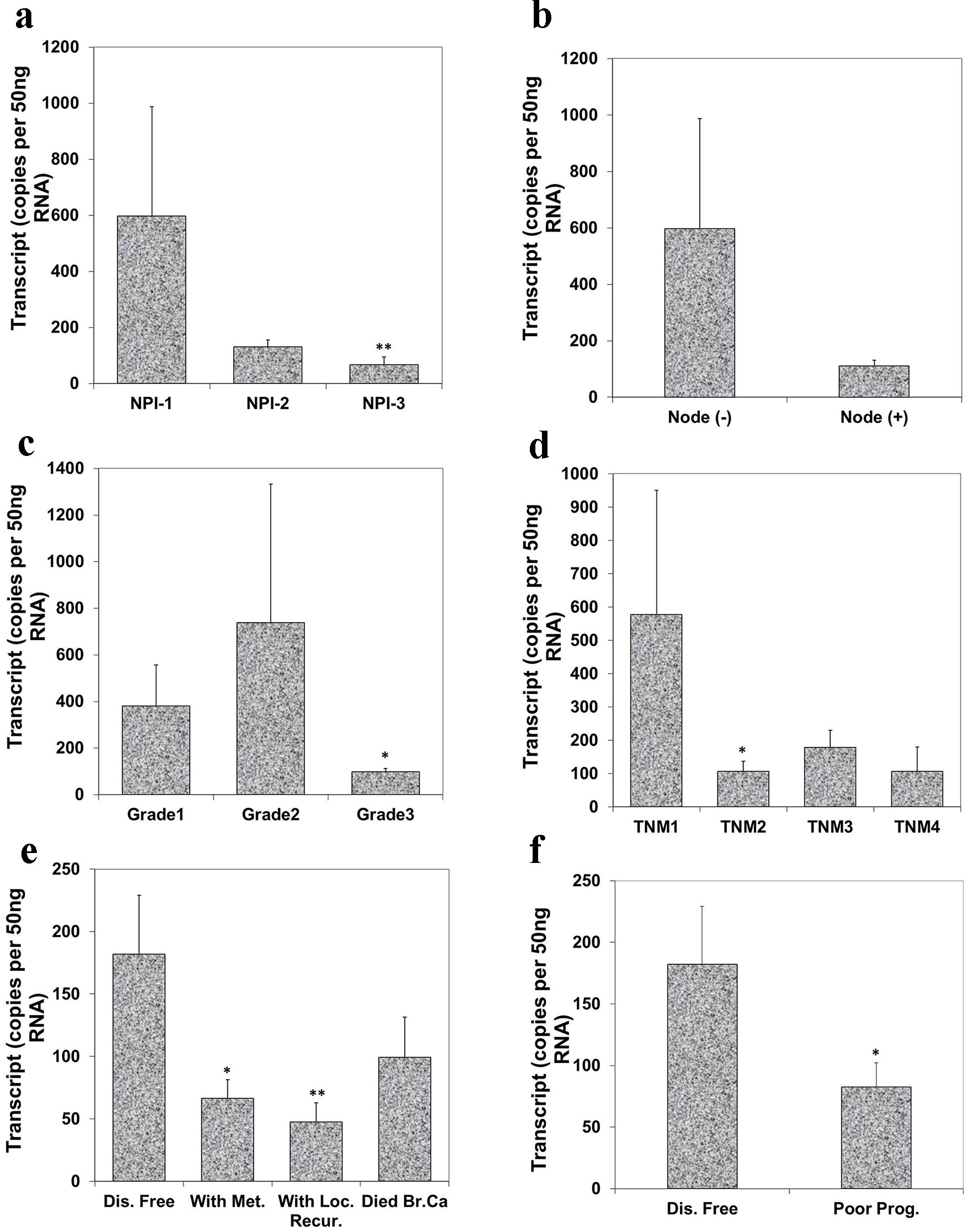
Figure 3. Correlation of Aurora kinase A expression with Nottingham prognostic index (NPI), grade, TNM staging and prognosis. (a) Lowest level of Aurora kinase A was observed in patients with poor prognostic index among these three groups (**P < 0.01 NPI-3 vs. NPI-1). (b) Node negative tumors had higher levels of Aurora kinase A transcript than node positive tumor. (c) Levels of expression of Aurora kinase A in breast tumor tissues in connection with grade and (d) with TNM status (*P < 0.05 grade 3 vs. grade 1; *P < 0.05 TNM 2 vs. TNM 1). (e) Levels of Aurora kinase A transcript and clinical outcomes. Aurora kinase A expression progressively decreased in the patients with metastasis disease, with local recurrence and die of breast cancer, compared with patient with disease free (*P < 0.05 metastasis vs. disease free; **P < 0.01 local recurrence vs. disease free). (f) Lower level of Aurora kinase A expression in patients with poor prognosis.
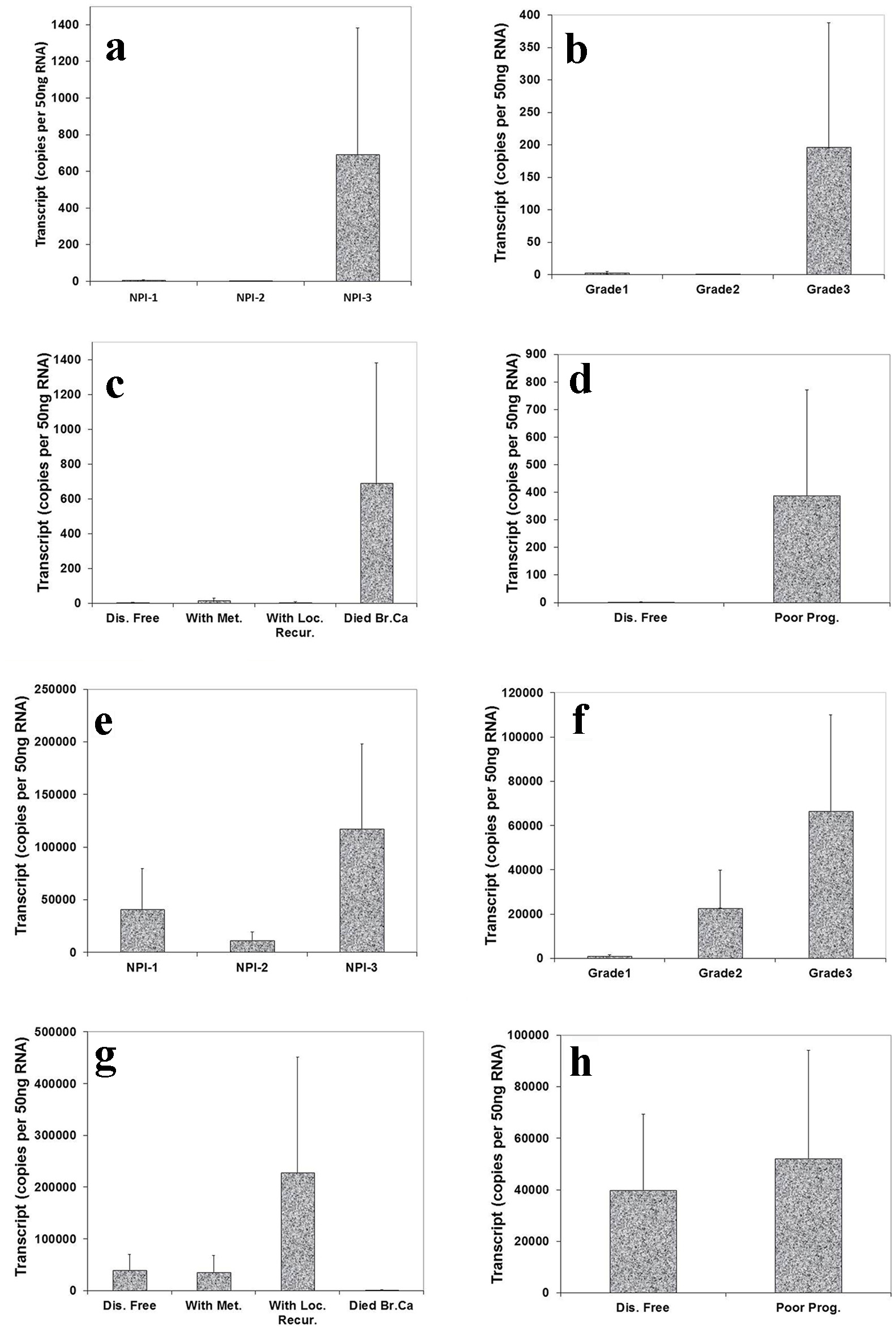
Figure 4. Correlation of Aurora kinase B and C expression with Nottingham prognostic index (NPI), grade staging and prognosis. Top panel (Aurora kinase B): (a) Highest level of Aurora kinase B in patients with poor prognostic index among these three groups. (b): Grade 3 tumor had higher level of Aurora kinase B transcript than grade 1 and 2. (c) Levels of Aurora kinase B transcript and clinical outcomes. Aurora kinase B expression progressively increased in the patients with local recurrence and die of breast cancer, compared with patient with disease free. (d) Higher level of Aurora kinase B expression in patients with poor prognosis. Bottom panel (Aurora kinase C): (e) Higher level of Aurora kinase C in patients with poor prognostic index than with moderate and poor prognosis. (f) A stepwise increase of levels of Aurora kinase C was found from grade 1 to grade 3 staging. (g) Lever of Aurora kinase C expression was higher in the patients with local recurrence than with metastasis disease and disease free. (h) Lower level of Aurora kinase C expression in patients with good prognosis.
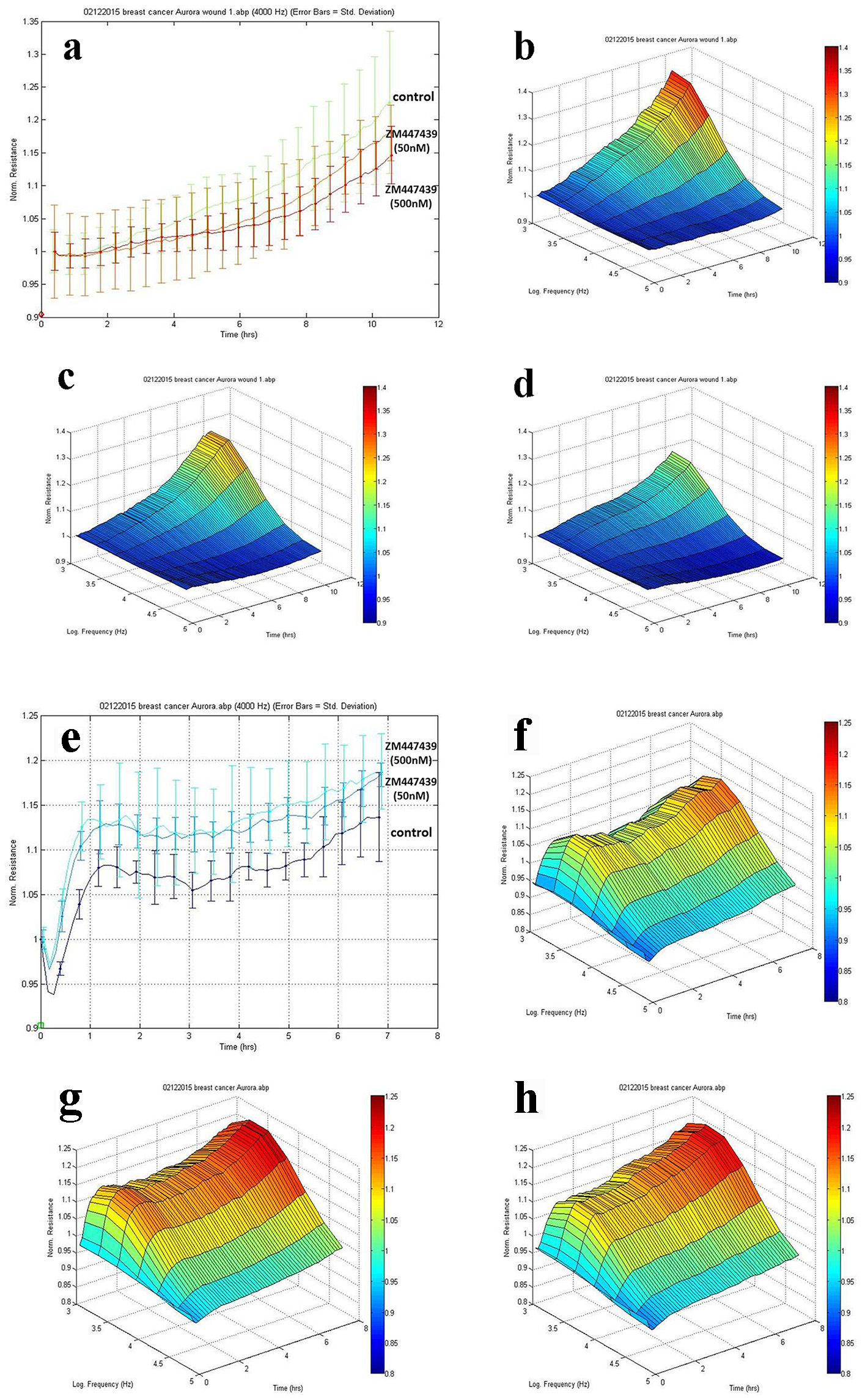
Figure 5. Effects of Aurora kinases inhibitor on the adhesion of breast cancer cells. Top panel: The response of MCF-7 to ZM447439. (a) Migration traces of MCF-7 cell’s response to ZM447439 at different concentrations. (b) 3D image of MCF-7 (control); (c and d) Response of MCF-7 to ZM447439 at 50 and 500 nM, respectively. Bottom panel: The response of MDA-MB-231 to ZM447439. (e) Traces of MDA-MB-231 cell’s response to ZM447439 at different concentrations. (f) 3D image of MDA-MB-231 (control); (g and h) Response of MDA-MB-231 to ZM447439 at 50 and 500 nM, respectively.
Tables
Table 1. Breast Cancer Patient Clinical Data Details
| Clinical data | Sample no. |
|---|
| Tissue sample | |
| Normal | 34 |
| Tumor | 118 |
| NPI | |
| 1 | 63 |
| 2 | 36 |
| 3 | 15 |
| Tumor grade | |
| 1 | 21 |
| 2 | 41 |
| 3 | 7 |
| TNM staging | |
| I | 2 |
| II | 36 |
| III | 7 |
| IV | 4 |
| Survival status | |
| 1 | 84 |
| 2 | 6 |
| 3 | 5 |
| 4 | 16 |
Table 2. Primers Sequences (Q-PCR)
| Molecular | Sense primers (5′-3′) | Antisense primers (5′-3′) |
|---|
| Aurora kinase A | GGTCAGTACATGCTCCATCT | ACTGAACCTGACCGTACACAGAGATCCACCTTCTCATC |
| Aurora kinase B | GCAGAGAGATCGAAATCCA | ACTGAACCTGACCGTACAGGGGCATACTCTAGGAATCAA |
| Aurora kinase C | TGGAGTGCTCTGCTATGAG | ACTGAACCTGACCGTACCGTACAGCATTGATAGTGGAAACCTC |
| GAPDH (Q-PCR) | CTGAGTACGTCGTGGAGTC | ACTGAACCTGACCGTACAGAGATGATGACCCTTTTG |




