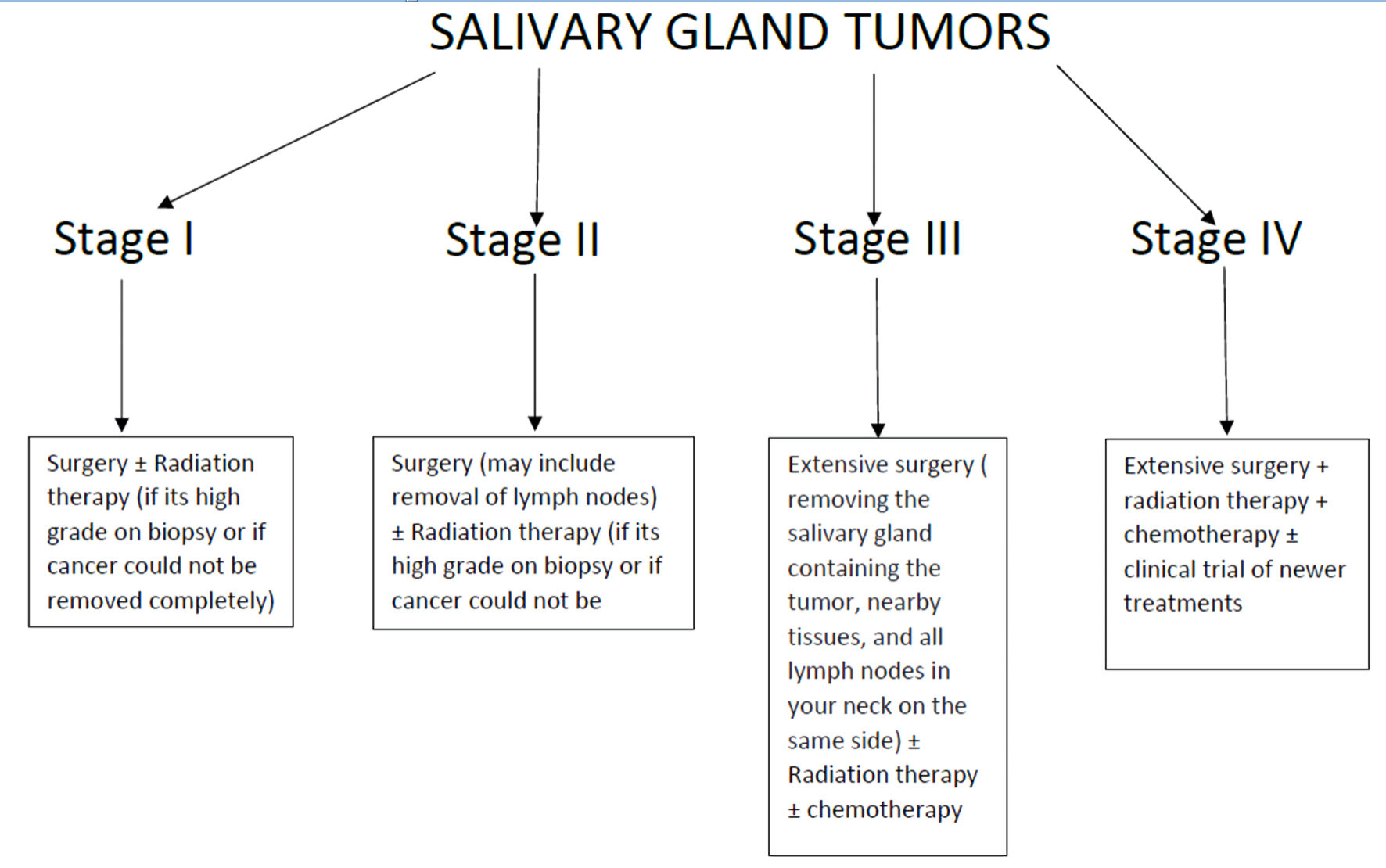
Figure 1. Stage-based management strategy for mucoepidermoid carcinoma.
| World Journal of Oncology, ISSN 1920-4531 print, 1920-454X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, World J Oncol and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.wjon.org |
Review
Volume 13, Number 1, February 2022, pages 1-7
Advances in the Treatment of Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
Figure

Tables
| Stage I | Noninvasive tumors with no spread to lymph nodes and no distant metastasis |
| Stage II | An invasive tumor with no spread to lymph nodes and no distant metastasis |
| Stage III | Smaller tumors (< 4 cm) that have spread to regional lymph nodes but no signs of metastasis |
| Stage IVA | Any invasive tumors with either no lymph node involvement or spread to only a single same-sided lymph node, but no metastasis |
| Stage IVB | Any cancer, with more extensive spread to lymph nodes but no metastasis |
| Stage IVC | Any cancer with distant metastasis |
| Author | Regimen | Number of patients | Number of objective responses |
|---|---|---|---|
| VNB: vinorelbine. | |||
| Airoldi et al, 2001 [19] | Cisplatin, 80 mg/m2 on day 1, plus VNB 25 mg/m2, on days 1 and 8, every 3 weeks | 16 | 0 |
| Gilbert et al, 2006 [20] (NCT01096407) | Paclitaxel 200 mg/m2 every 3 weeks | 50 | 3 |
| Locati et al, 2016 [23] (NCT01703455) | Sorafenib 400 mg orally every 12 h continuously in 4-week cycle | 37 | 2 |
| Kim et al, 2017 [24] (NCT02558387) | Nintedanib 200 mg daily on a continuous schedule until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or patient withdrawal. Tumor response was assessed every two cycles. | 20 | - |
| Raguse et al, 2004 [21] | Docetaxel 100 mg/m2 every 3 weeks | 4 | 4 |
| Haddad et al, 2003 [22] | Trastuzumab 4 mg/kg loading dose, 2 mg/kg weekly after that | 14 | 1 |
| Agulnik et al, 2007 [25] | Lapatinib 1,500 mg daily | 40 | 0 |
| Targeted agent | Oncogenes involved in MEC |
|---|---|
| MEC: mucoepidermoid carcinoma; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR: VEGF receptor; FGFR: fibroblast growth factor receptor; PDGFR: platelet-derived growth factor receptor; HER2/neu: human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; erbB-2: receptor tyrosine-protein kinase; TrkB: tropomyosin receptor kinase B; BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor. | |
| Sorafenib | VEGF and ANG2 |
| Nintedanib | VEGFR, FGFR, and PDGFR |
| Trastuzumab | HER2/neu |
| Lapatinib | EGFR and erbB2 |
| ANA-12 | TrkB and BDNF |