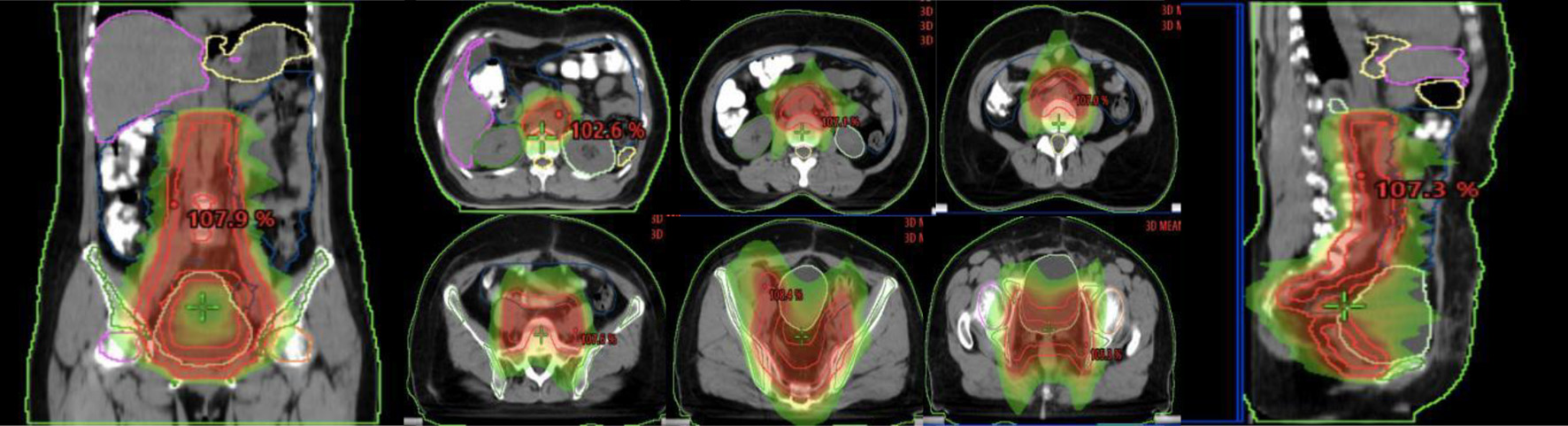
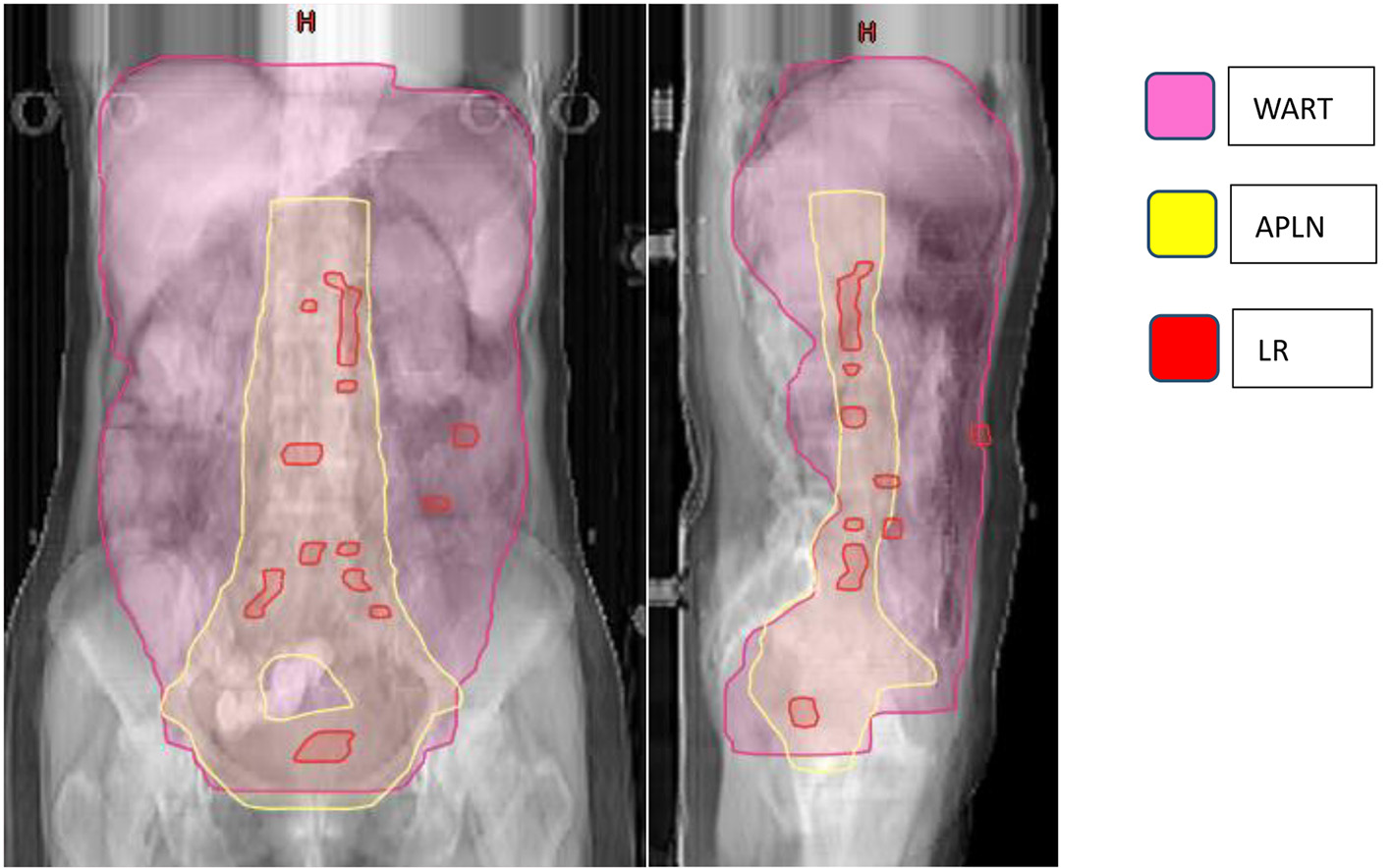
Figure 1. Illustration of the abdominopelvic lymphatic drainage area irradiation.
| World Journal of Oncology, ISSN 1920-4531 print, 1920-454X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, World J Oncol and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.wjon.org |
Original Article
Volume 13, Number 3, June 2022, pages 145-154
Abdominopelvic Lymphatic Drainage Area Irradiation for Consolidative Radiotherapy of Advanced Ovarian Carcinoma: Analysis of Clinical Application Efficacy and Dosimetric Verification
Figures

Tables
| Characteristics | Number | % |
|---|---|---|
| FIGO: Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics; CA125: carbohydrate antigen 125. | ||
| Age (years) | ||
| < 60 | 76 | 76.76 |
| ≥ 60 | 23 | 23.23 |
| Number of surgeries | ||
| < 2 | 56 | 56.57 |
| ≥ 2 | 43 | 43.43 |
| Histology | ||
| Epithelial carcinoma | 92 | 92.93 |
| Interstitial tumors of the sex cords | 5 | 5.05 |
| Germ cell tumors | 2 | 2.02 |
| FIGO stage | ||
| III | 89 | 89.90 |
| IV | 10 | 10.10 |
| Preoperative CA125 | ||
| < 100 | 55 | 55.56 |
| ≥ 100 | 44 | 44.44 |
| Postoperative chemotherapy courses | ||
| < 6 | 17 | 17.17 |
| ≥ 6 | 82 | 82.93 |
| CA125 decreased to normal | ||
| < 3 chemotherapy courses | 53 | 53.54 |
| ≥ 3 chemotherapy courses | 46 | 46.46 |
| Failure mode | No. | % |
|---|---|---|
| APLN: abdominopelvic lymphatic drainage area irradiation. | ||
| Local recurrence | 2 | 2.02 |
| Distant metastasis | 32 | 32.32 |
| Local recurrence and distant metastasis | 18 | 18.18 |
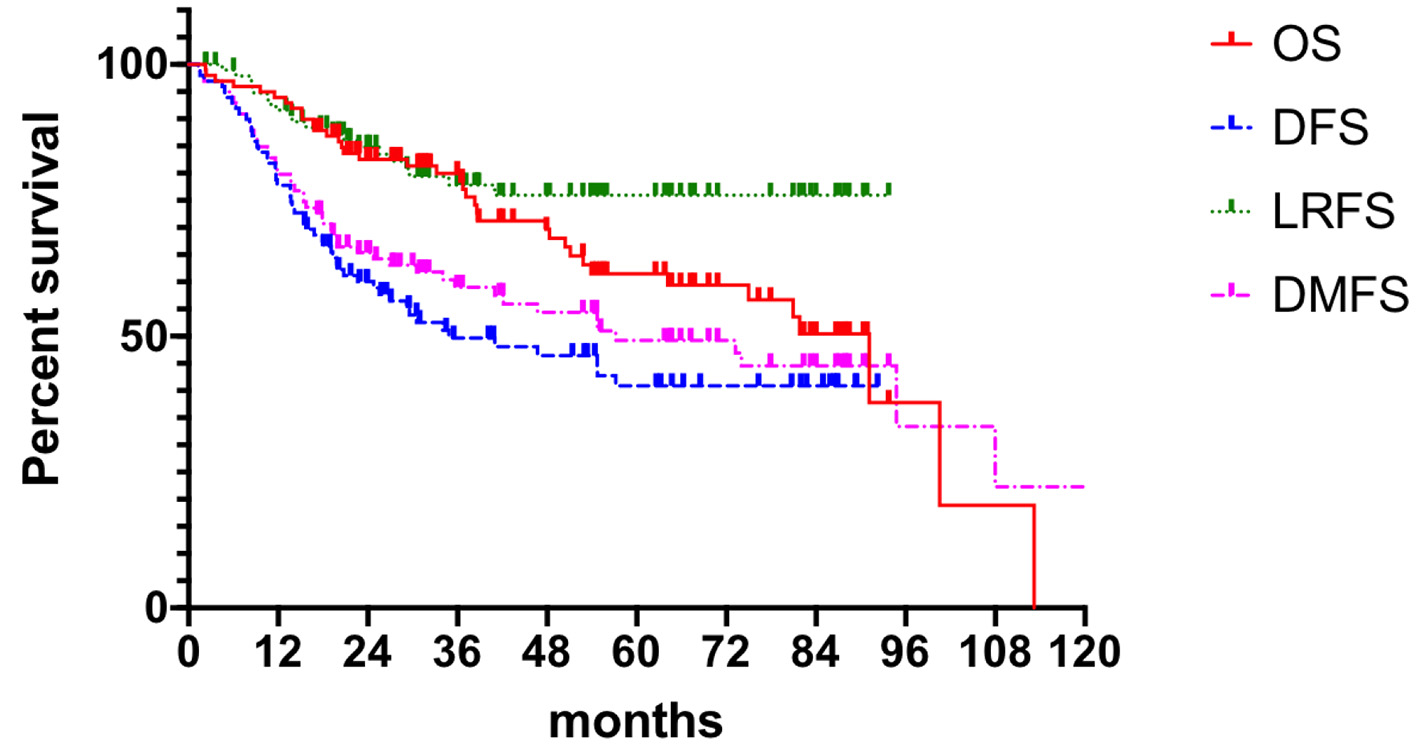
| n | OS (%) | P value | DFS (%) | P value | LRFS (%) | P value | DMFS (%) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Statistically significant difference (paired, two-tailed t-test, P < 0.05). OS: overall survival; DFS: disease-free survival; LRFS: local recurrence free survival; DMFS: distant metastasis free survival; FIGO: Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics; CA125: carbohydrate antigen 125. | |||||||||
| Age (years) | |||||||||
| < 60 | 76 | ||||||||
| ≥ 60 | 23 | ||||||||
| Number of surgeries | 0.999 | ||||||||
| < 2 | 56 | 67.9 | 0.491 | 52.6 | 0.569 | 82.7 | 0.049* | 63.4 | |
| ≥ 2 | 43 | 53.5 | 45.9 | 65.8 | 71.9 | ||||
| Surgical resection status | 0.761 | ||||||||
| Complete resection | 70 | 62.9 | 0.910 | 49.0 | 0.321 | 72.6 | 0.717 | 74.7 | |
| Basic resection | 21 | 66.7 | 56.1 | 81.5 | 57.4 | ||||
| Major resection | 8 | 37.5 | 32.2 | 66.2 | 55.5 | ||||
| Histology | 0.385 | ||||||||
| Epithelial carcinoma | 92 | 62.0 | 0.945 | 49.3 | 0.823 | 77.4 | 0.222 | 64.0 | |
| Interstitial tumors of the sex cords | 5 | 60.0 | 46.4 | 47.0 | 48.5 | ||||
| Germ cell tumors | 2 | 50.0 | 42.6 | 43.4 | 43.4 | ||||
| FIGO stage | 0.128 | ||||||||
| III | 89 | 61.6 | 0.151 | 50.2 | 0.055 | 78.8 | 0.819 | 70.8 | |
| IV | 10 | 50.0 | 20.2 | 48.8 | 24.0 | ||||
| Preoperative CA125 (U/mL) | 0.512 | ||||||||
| < 100 | 48 | 64.6 | 0.616 | 48.4 | 0.716 | 79.2 | 0.773 | 74.6 | |
| ≥ 100 | 41 | 61.6 | 50.0 | 75.9 | 48.9 | ||||
| Postoperative chemotherapy courses | 0.332 | ||||||||
| < 6 | 17 | 70.6 | 0.064 | 54.8 | 0.652 | 76.5 | 0.769 | 58.8 | |
| ≥ 6 | 82 | 61.6 | 50.0 | 79.8 | 46.2 | ||||
| CA125 decreased to normal | 0.523 | ||||||||
| < 3 chemotherapy courses | 53 | 60.4 | 0.794 | 48.3 | 0.842 | 77.4 | 0.920 | 57.5 | |
| ≥ 3 chemotherapy courses | 46 | 66.7 | 50.0 | 79.8 | 70.8 | ||||
| Characteristic | P-value | HR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Statistically significant difference (paired, two-tailed t-test, P < 0.05). LRFS: local recurrence free survival; HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval; CA125: carbohydrate antigen 125. | |||
| Number of surgeries | < 2 | 0.048* | 2.708 (1.009 - 7.266) |
| ≥ 2 | |||
| Surgical resection status | Complete resection | 0.939 | 0.969 (0.427 - 2.199) |
| Basic resection | |||
| Major resection | |||
| Postoperative chemotherapy courses | < 6 | 0.963 | 1.015 (0.548 - 1.880) |
| ≥ 6 | |||
| CA125 decreased to normal | < 3 chemotherapy courses | 0.291 | 0.808 (0.544 - 1.200) |
| ≥ 3 chemotherapy courses | |||
| Histology | Epithelial carcinoma | 0.096 | 2.444 (0.854 - 6.992) |
| Interstitial tumors of the sex cords | |||
| Germ cell tumors | |||
| APLN, mean dose (Gy) | WART, mean dose (Gy) | Difference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Statistically significant difference (paired, two-tailed t-test, P < 0.05). PTV: planning target volume; APLN: abdominopelvic lymphatic drainage area irradiation; WART: whole abdominal radiotherapy. | |||
| PTV | 46.38 ± 0.20 | 31.30 ± 0.24 | 15.08 ± 0.43* |
| Liver | 4.27 ± 3.01 | 29.54 ± 1.14 | -25.27 ± 3.63* |
| Spleen | 4.55 ± 2.52 | 29.25 ± 3.04 | -24.71 ± 3.91* |
| Kidney R | 10.21 ± 3.58 | 18.98 ± 2.65 | -8.77 ± 5.03* |
| Kidney L | 9.75 ± 2.83 | 18.43 ± 3.36 | -8.68 ± 5.89* |
| Small intestine | 23.50 ± 1.56 | 31.64 ± 0.26 | -8.14 ± 1.51* |
| Femoral R | 25.26 ± 2.08 | 18.93 ± 1.16 | 6.32 ± 2.61* |
| Femoral L | 25.49 ± 1.58 | 18.23 ± 0.98 | 7.26 ± 1.44* |
| Bladder | 35.11 ± 3.23 | 29.41 ± 2.02 | 5.70 ± 4.24* |
| Rectum | 39.68 ± 3.29 | 25.64 ± 3.15 | 14.04 ± 4.01* |
| Bone marrow | 27.77 ± 2.87 | 22.84 ± 0.82 | 4.93 ± 2.90* |
| Stomach | 7.14 ± 5.88 | 31.56 ± 0.33 | -24.42 ± 5.72* |
| Spine cord | 18.05 ± 2.19 | 21.10 ± 1.31 | -3.05 ± 2.00* |
| TCP (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APLN | WART | ||||||||
| APLN (TCD50=30) | 96.95 | 53.68 | |||||||
| APLN (TCD50=40) | 76.20 | 10.13 | |||||||
| APLN (TCD50=38) | 82.84 | 14.65 | |||||||
| NTCP (%) | |||||||||
| Small intestine | Kidney | Liver | Spine cord | ||||||
| *Statistically significant difference (paired, two-tailed t-test, P < 0.05). APLN: abdominopelvic lymphatic drainage area irradiation; WART: whole abdominal radiotherapy. | |||||||||
| APLN | 1.05 | 0.04 | 0.01 | < 0.001 | |||||
| WART | 0.02 | 2.99 | 0.77 | < 0.001 | |||||
| Difference | 1.04* | 0.19* | 0.04* | - | |||||
| Author | Type of study | Reported stage | Population | Trial design | Radiation therapy dose | Outcomes | Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT: chemotherapy; WART: whole abdominal radiotherapy; OS: overall survival; WHO: World Health Organization; GI: gastrointestinal; CRT: chemoradiotherapy; PFS: progression-free survival; SIB: simultaneous integrated boost; IMRT: intensity-modulated radiotherapy; PTV: planning target volume; DFS: disease-free survival; HT: helical tomotherapy. | |||||||
| Bruzzone et al [15] | Randomized trial | Stage III-IV (minimal residual disease) | 41 total (21 in CT arm and 20 in WART arm) | CT arm (three additional courses of the same front-line CT) and WART arm | 43.2 Gy/24 fractions to the pelvis and 30.2 Gy to the upper abdomen | 3-year OS (CT arm): 85%; 3-year OS (WART arm): 45% | CT arm - grade 3 N/V events (WHO): 36.9%; WART arm - grade 3 N/V events (WHO): 14.2%; bowel obstruction: 5% |
| North Thames Ovary Group Study [16] | Randomized trial | Stage IIB-IV (≤ 2 cm residual disease ) | 117 total (59 in CT arm and 58 in WART arm) | CT arm (five additional courses of carboplatin-based CT) and WART arm | 24 Gy/20 fractions/5 #, boost up to a dose of 40 Gy (residual disease) | 5-year OS (CT arm): 30%; 5-year OS (WART arm): 25% | CT arm - grade 4 N/V events (WHO): 2%; WART arm - grade 3 myelotoxicity (WHO): 5%; WART arm - bowel obstruction (WHO): 1.7% |
| Pickel et al [17] | Randomized trial | Stage IC-IV (no clinical disease) | 64 total (32 IN WART arm and 32 in observation arm) | Surgery (no residual disease) and adjuvant platinum-based CT and randomization to WART arm and observation arm | WART: 30 Gy (1.5 Gy/5 treatments per week). Additional boost of 21.6 Gy to the pelvis and boost of 12 Gy to para-aortic region | 5-year OS: 59%; 5-year OS: 33% | Treatment breaks: 37.5%; bowel obstruction: 3.1% |
| Swedish-Norwegian Ovarian Cancer Study Group [18] | Prospective randomized trial | Stage III | 172 total (98 in CRT arm and 74 in observation arm) | Randomization to: consolidation with RT (WART); consolidation with CT (six courses); observation | Abdominal RT dose of 20 Gy (1 Gy, 5 days a week, 20 fractions) + abdominopelvic boost dose of 20.4 Gy (1.7 Gy per fraction, 12 fractions) | 5-year PFS: 56.3%; 5-year OS: 68.8%; 5-year PFS: 36%; 5-year OS: 57.1% | Early side events radiotherapy group: grade 3 myelotoxicity: 4.4%; grade 3 bowel events: 4.4%; late side events radiotherapy group: grade 3 intestinal obstruction: 10% |
| Stevens et al [21] | Pre-approved | Ic1-IIIa2 | Five patients | SIB-WART (IMRT) | 25 Gy (PTV_Low) and SIB 45 Gy (PTV_High), 25 fractions | All DFS (median follow-up: 77 months) | One grade 3 GI. Two grade 2 osteoporotic fragility fractures |
| Shetty et al [22] | A feasibility study | IIc-IIIc | Eight patients | SIB-WART (HT) | 25 Gy/25 fractions and SIB 45 Gy/25 fractions | Three recurrences in peritoneum (median follow-up: 15 months) | One grade 3 GI |