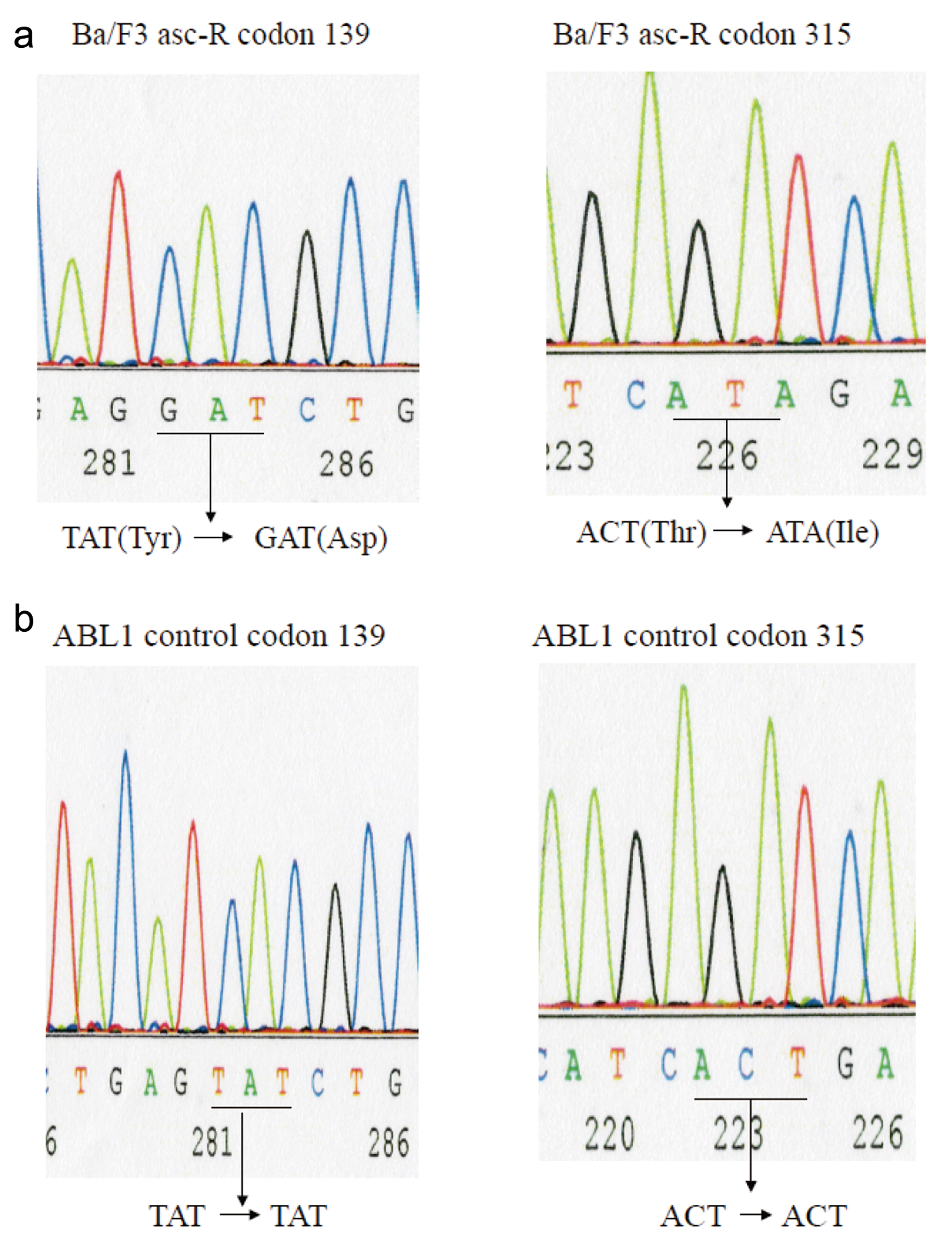
Figure 1. BCR-ABL kinase domain mutation analysis. Mutation screening via sequence analysis was performed to identify the ABL kinase domain in Ba/F3-asciminib-R (Ba/3 asc-R) cells (a) and normal control samples (b). Direct sequencing to detect mutations in the ABL kinase domain in the cell lines revealed Y139D and T315I mutations in Ba/F3 asc-R cells.
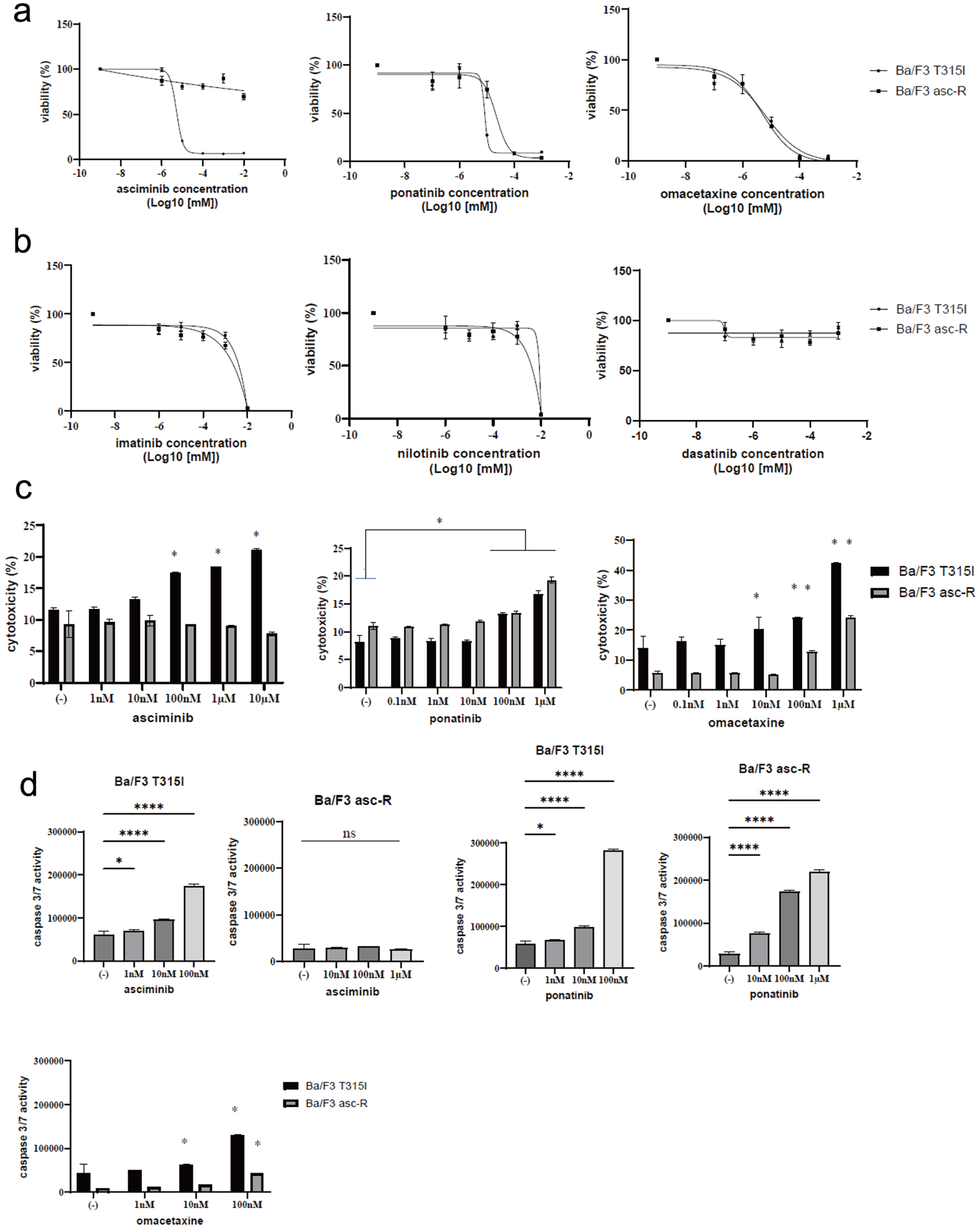
Figure 2. Activity of ABL inhibitors in Ba/F3-asciminib-R (Ba/F3 asc-R) and Ba/F3 T315I cells. (a) Ba/F3 asc-R and Ba/F3 T315I cell lines were cultured with the indicated concentrations of asciminib, ponatinib, or omacetaxine for 72 h. Cell growth was evaluated using Cell Counting Kit-8. (b) Ba/F3 asc-R and Ba/F3 T315I cell lines were cultured with the indicated concentrations of imatinib, nilotinib, or dasatinib for 72 h. Cell growth was evaluated using Cell Counting Kit-8. (c) Ba/F3 asc-R and Ba/F3 T315I cell lines were cultured with the indicated concentrations of asciminib, ponatinib, or omacetaxine for 72 h. Cell death was evaluated using a Cytotoxicity LDH Assay Kit. *P < 0.05 compared to control. (d) Ba/F3 asc-R and Ba/F3 T315I cell lines were cultured with the indicated concentrations of asciminib, ponatinib, or omacetaxine for 48 h. Caspase 3/7 activity was evaluated. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001 compared to control. ns: not significant.

