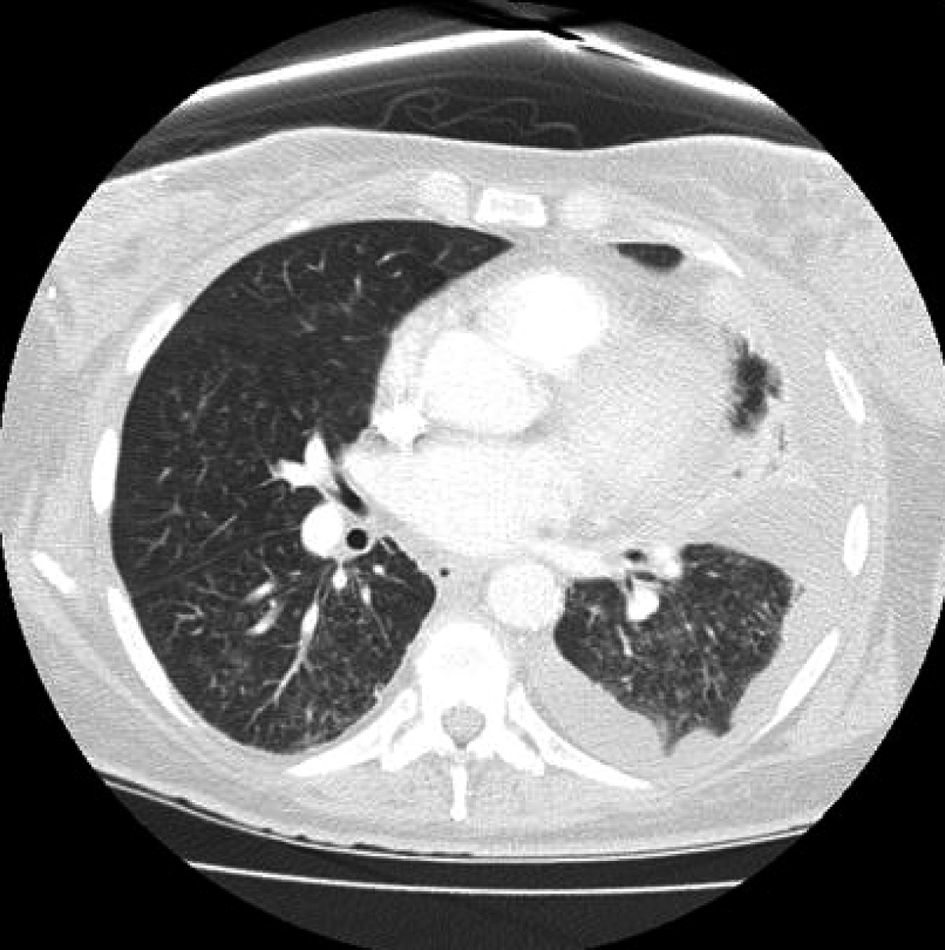
Figure 1. Sudden onset of diffuse interstitial infiltrates and left sided pleural effusion.
| World Journal of Oncology, ISSN 1920-4531 print, 1920-454X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, World J Oncol and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.wjon.org |
Case Report
Volume 3, Number 4, August 2012, pages 194-198
Early Recognition of Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome Leads to Avoidance of Endotracheal Intubation
Figures

Tables
| Category | Mechanism | Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Abbreviations: NK: natural killer cells; Th: helper T cells; IRIS: immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor alpha; GMI: galactomannan index; KIRs: killer immunoglobulin like receptors; N/A: non-applicable. | ||
| Proliferation of Th1 and Th17 cells | Proinflammatory. Activate macrophages. Promote NK cell cytotoxicity. Cause IRIS. Involved in solid organ transplant rejection. | Corticosteroids (decrease Th1). Statins (decrease Th1 and Th17). Infliximab for steroid refractory cases (TNF-α antagonist which inhibits macrophages). |
| Suppression of Th2 and regulatory T cells | Usually are anti-inflammatory and leads to tolerance but reduction in levels in IRIS potentiates inflammation. | Corticosteroids (increase Th2 and regulatory T cells). Statins (increase Th2 and regulatory T cell responses). |
| Leukotrienes | Produced by mast cells. Proinflammatory. | Monteleukast |
| Genetic predisposition | Ancestral haplotype HLA A2, B44, DR4. Regulatory cytokine gene polymorphisms of IL-6 and TNF-α | N/A |
| Unmasking IRIS | Immune response to covert infection (viable pathogen antigens) such as chronic disseminated candidiasis in neutropenic hematological malignancy patients after neutrophil recovery. | Antifungals. Corticosteroids. |
| Paradoxical IRIS | Immune response to nonviable dead pathogen debris, tumor antigens or host antigens. For example pulmonary IRIS after neutrophil recovery in effectively treated invasive pulmonary aspergillosis with decrease in serum GMI. | Corticosteroids |
| Natural killer cells | Activating KIRs encoded by KIR genes 3DS1 and 2DS5 more common in patients with IRIS. | N/A |
| Clinical Criteria | Laboratory Values |
|---|---|
| Temporal association with rapid onset of neutrophil recovery | absolute neutrophil count recovery < 100/microliter to > 4500/microliter within 5 days |
| Paradoxical onset of clinical and radiologic deterioration despite effective antimicrobial therapy | Exclusion of other causes. All cultures negative (blood, urine, sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage) and/or > 50% decrease in sequential serum galactomannan titers |
| Unmasking of covert infection (fever, abdominal pain) | New hepatosplenic lesions seen after neutrophil recovery, culture negative with liver biopsy showing granulomas with T cell infiltration (chronic disseminated candidiasis) |
| Granuloma formation in affected organ | Relies on Th 1 cytokines and 1 alpha-hydroxylase of activated macrophages increases synthesis of 1, 25 (OH)2 vitamin D3 causing hypercalcemia |