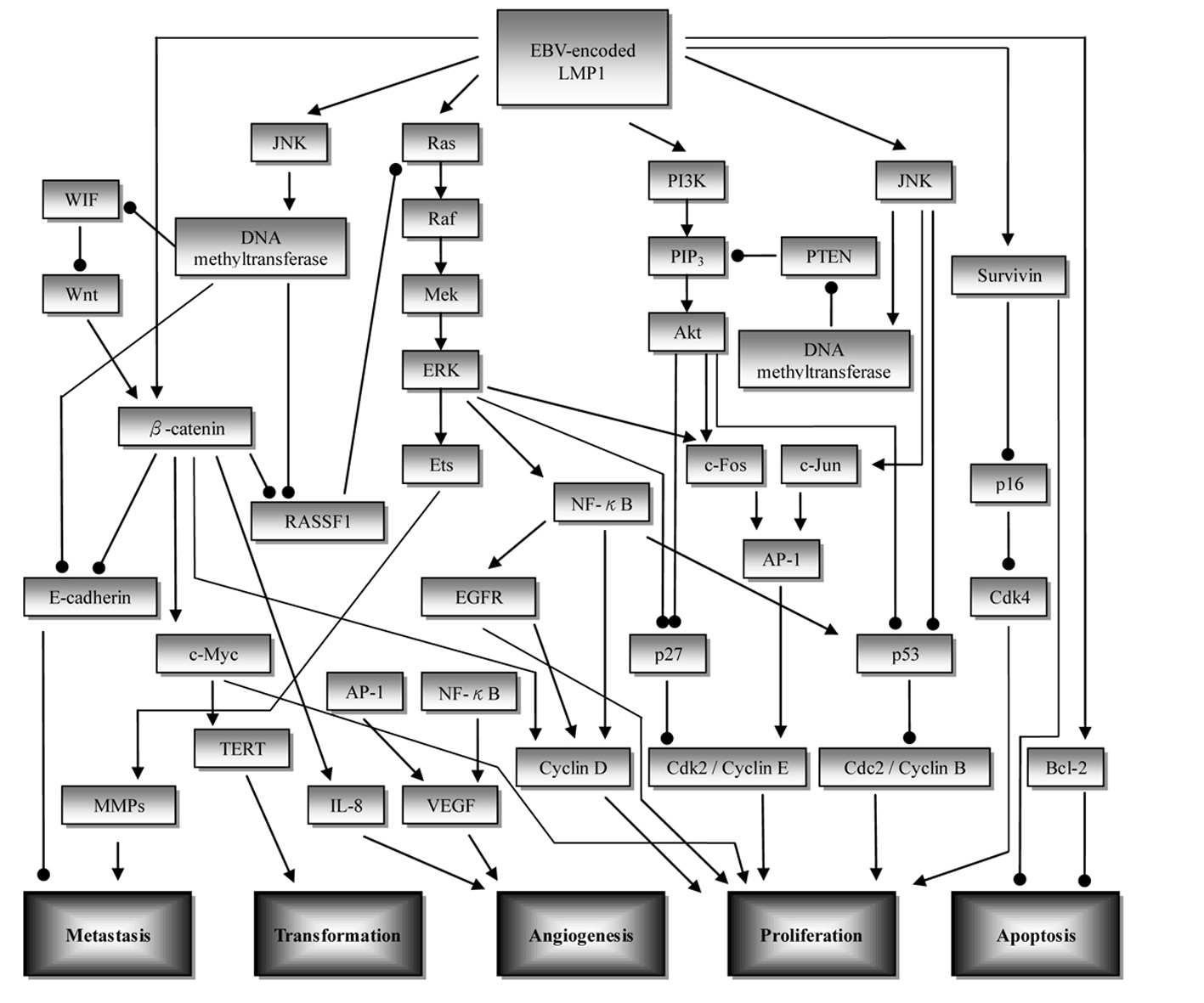
Figure 1. Overview of the signaling pathways involved in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) development. Initiation of upstream signaling proteins in the NPC development begins with LMP1. Subsequent induced activity of downstream proteins in several pathways such as β-catenin, NF-κB, and AP-1 leads to dysregulation of cell proliferation (CDK/cyclin protein), increase in angiogenesis (VEGF, IL-8), metastasis (E-cadherin, MMPs), cell transformation (TERT), and inhibition of apoptosis (survivin, Bcl-2). ——►: stimulatory effect; ——●: inhibitory effect; AP-1: activator protein 1; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; ERK: extracellular signal related kinase; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; LMP1: latent membrane protein 1; MMP: matrix metalloproteinase; PTEN: phosphatase and tensin homolog; PI3K: phosphoinositol-3-kinase; RASSF: Ras association domain family; TERT: telomerase reverse transcriptase; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor; WIF: Wnt inhibitory factor.