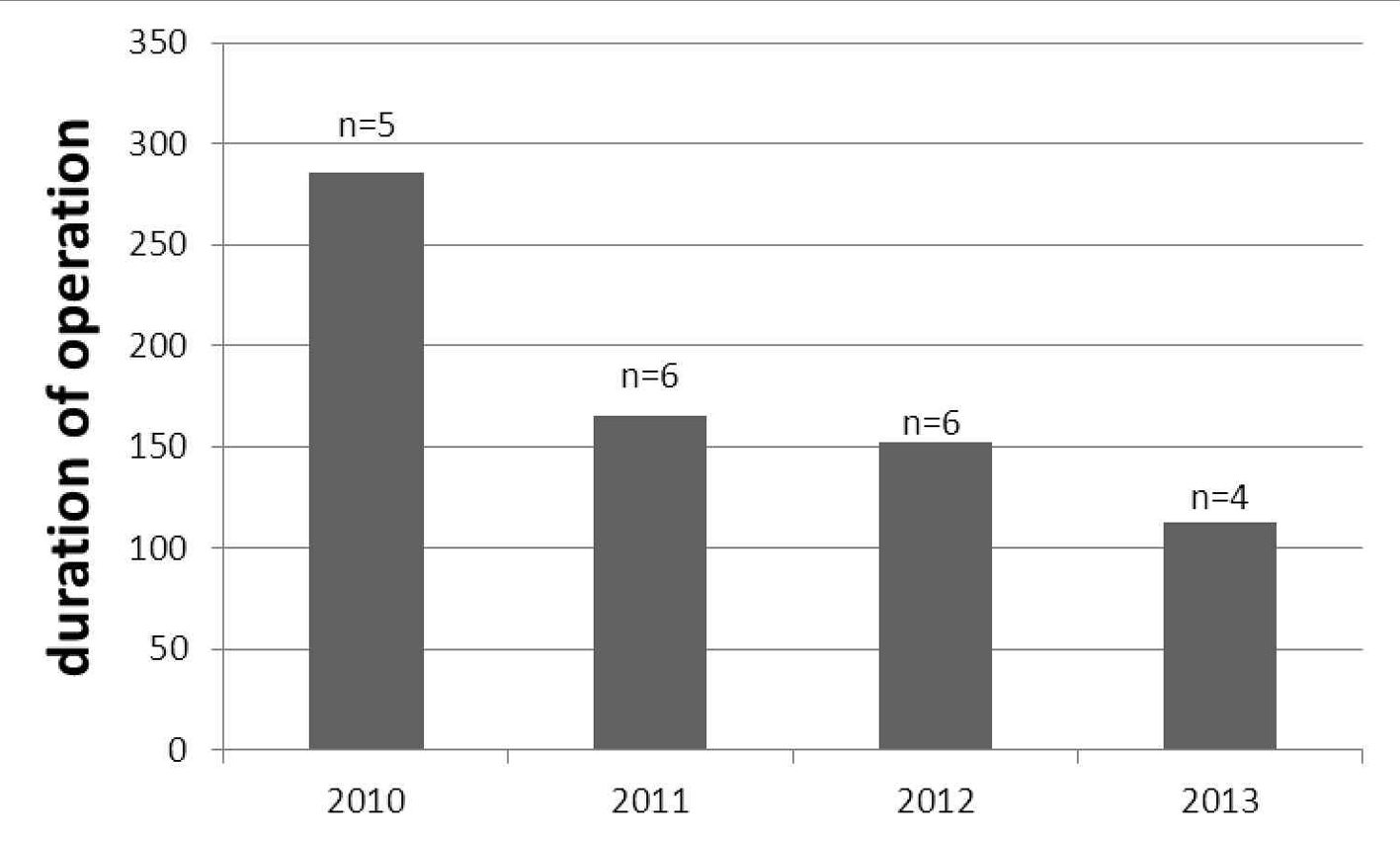
Figure 1. The decreasing duration of laparoscopic operation (minutes) among the years; number of operated patient shown with “n”.
| World Journal of Oncology, ISSN 1920-4531 print, 1920-454X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, World J Oncol and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.wjon.org |
Original Article
Volume 4, Number 6, December 2013, pages 235-240
Surgical Staging of Early Stage Endometrial Cancer: Comparison Between Laparotomy and Laparoscopy
Figures

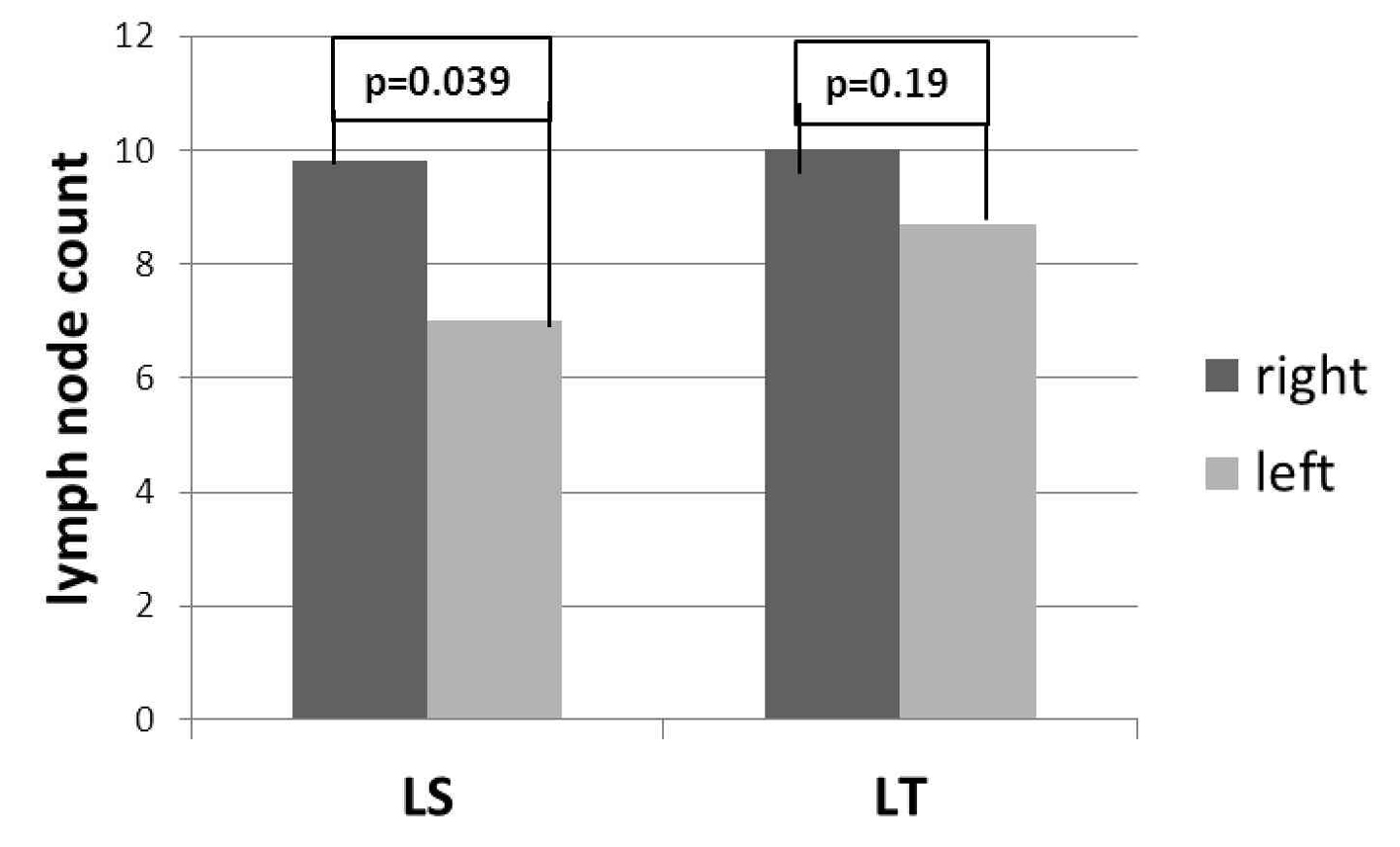
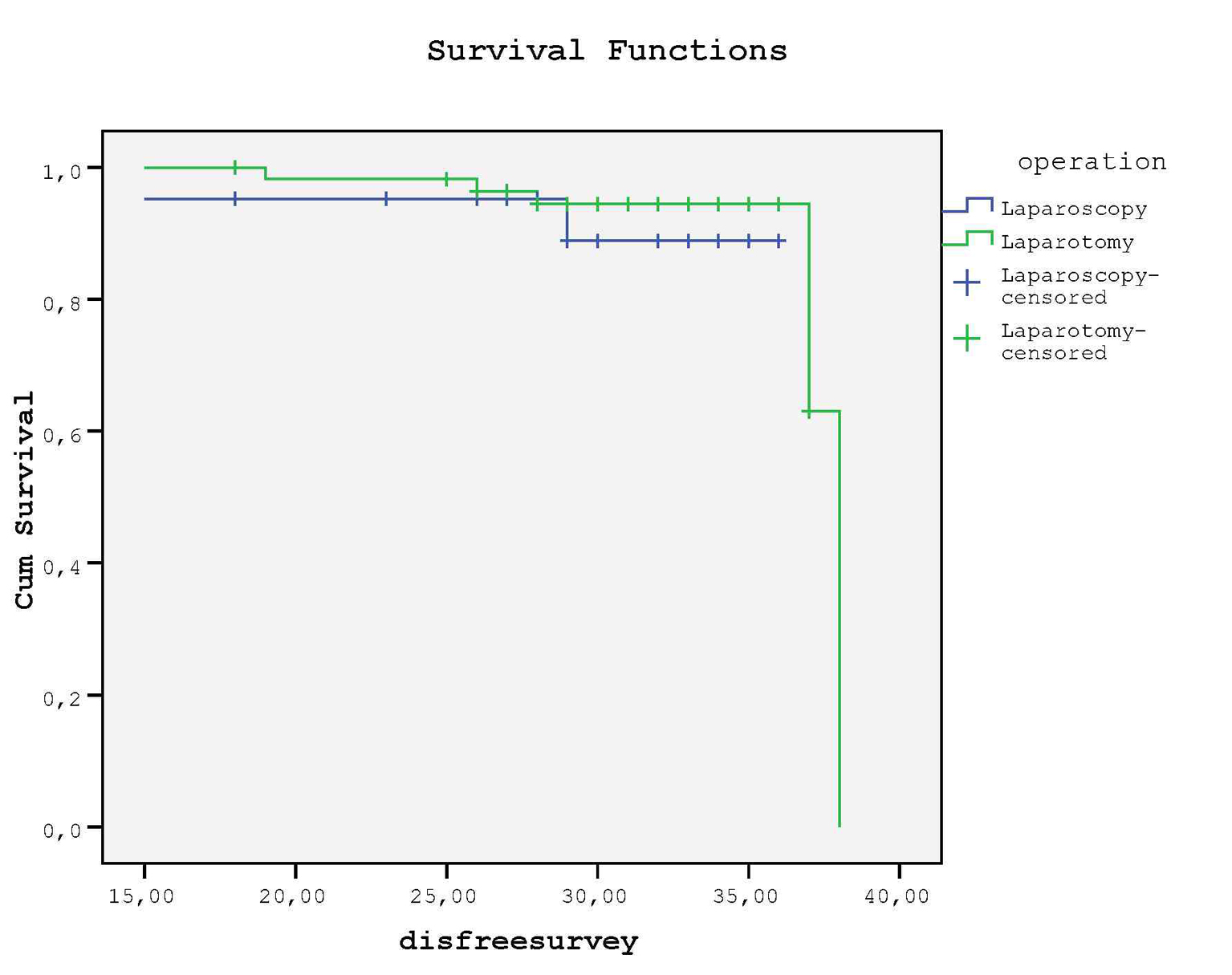
Tables
| Laparoscopy (n = 21) | Laparotomy (n = 58) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMI: body mass index; min.: minutes; sd: standard deviation. *P < 0.05. | |||
| Age (years), mean (range) | 56 (46-66) | 54 (43-65) | 0.47 |
| BMI, kg/m2, mean (± sd) | 26.8 (± 2.1) | 26.7 (± 2.6) | 0.85 |
| Tumor histology, n (%) | |||
| Endometrioid | 17 (80.9%) | 53 (91.3%) | 0.21 |
| Others | 4 (19.1%) | 5 (8.7%) | |
| Tumor grade, n (%) | |||
| Ι | 12 (22.2%) | 42 (77.8%) | 0.21 |
| ΙΙ | 9 (39.1%) | 14 (60.9%) | |
| ΙΙΙ | 0 | 2 (100%) | |
| Duration of operation (min.), mean (range) | 180.47 (112-248) | 169.65 (123-215) | 0.4 |
| Intraoperative bleeding (mL), mean (± sd) | 136.6 (± 33.9) | 245.6 (± 68.7) | < 0.0001* |
| Postoperative complications | |||
| Ileus | 3 | 2 | |
| Wound infection | 0 | 4 | |
| Evisceration | 0 | 1 | |
| Iliac artery injury | 1 | 2 | |
| Overall, n (%) | 4 (14.2%) | 9 (15%) | |
| Hospitalization period (day), mean (± sd) | 5 (± 1.3) | 8.5 (± 1.7) | < 0.0001* |
| Laparoscopy (n = 21) | Laparatomy (n = 58) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| sd: standard deviation. P < 0.05. | |||
| Pelvic lymphadenectomy, n (%) | 21 (100%) | 58 (100%) | |
| Dissected pelvic lymph node count, mean (± sd) | 9.2 (± 4.8) | 8.9 (± 5.3) | 0.8 |
| Paraaortic lymphadenectomy, n (%) | 6 (28.5%) | 27 (46.5%) | |
| Dissected paraaortic lymph node count, mean (± sd) | 3.1 (± 5.6) | 4.1(± 6) | 0.51 |