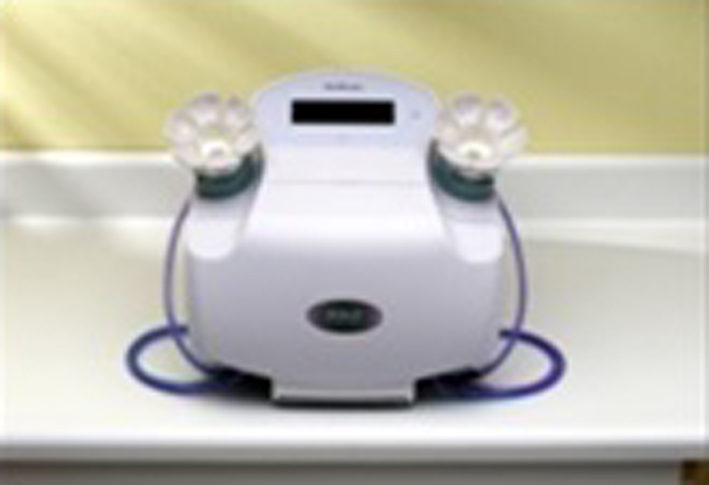

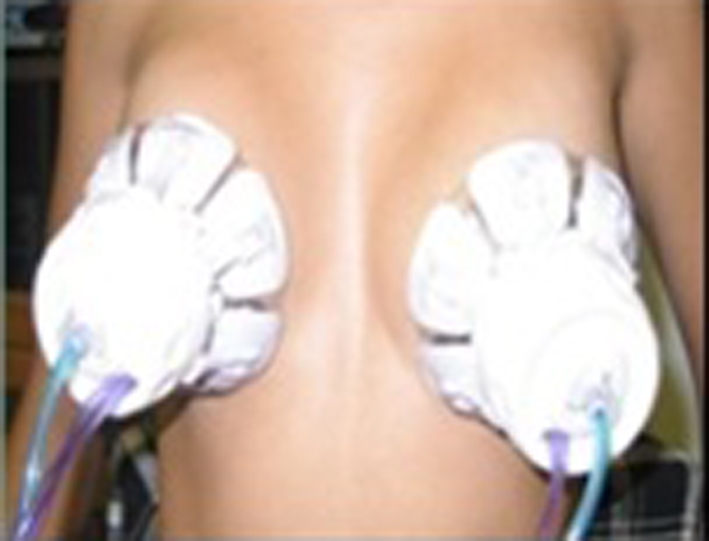
Figure 1. HAL breast test equipment.
| World Journal of Oncology, ISSN 1920-4531 print, 1920-454X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, World J Oncol and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.wjon.org |
Original Article
Volume 5, Number 4, August 2014, pages 166-174
Liquid-Based Medium Used to Prepare Cytological Breast Nipple Fluid Improves the Quality of Cellular Samples Automatic Collection
Figures


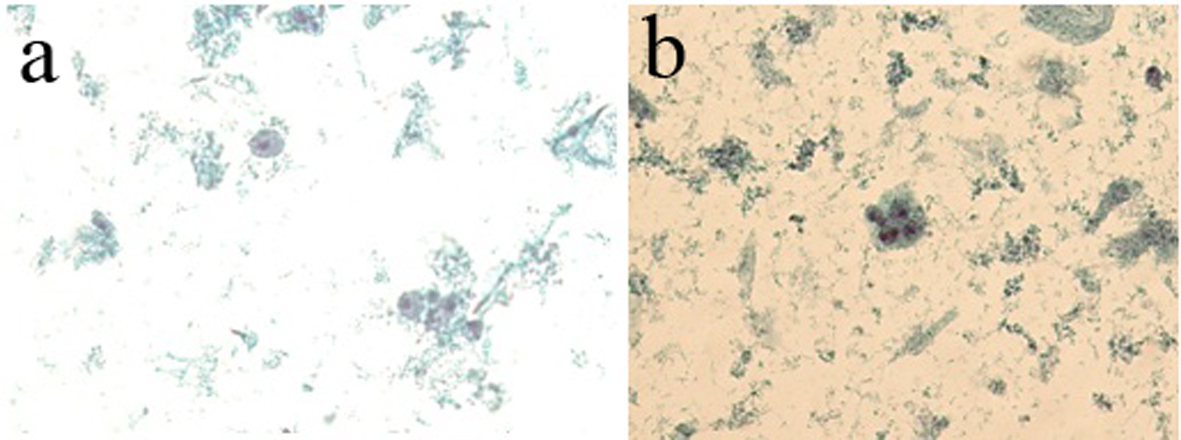
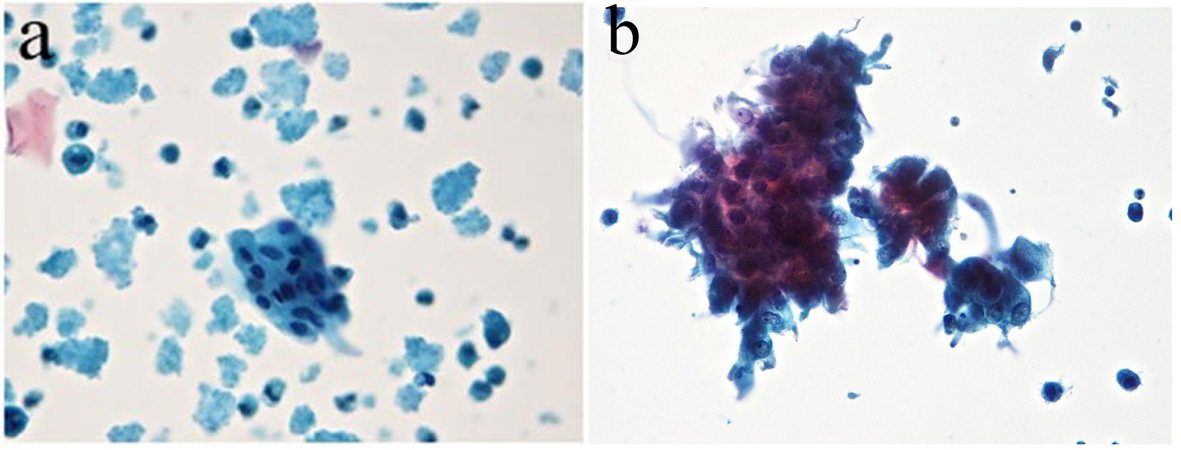
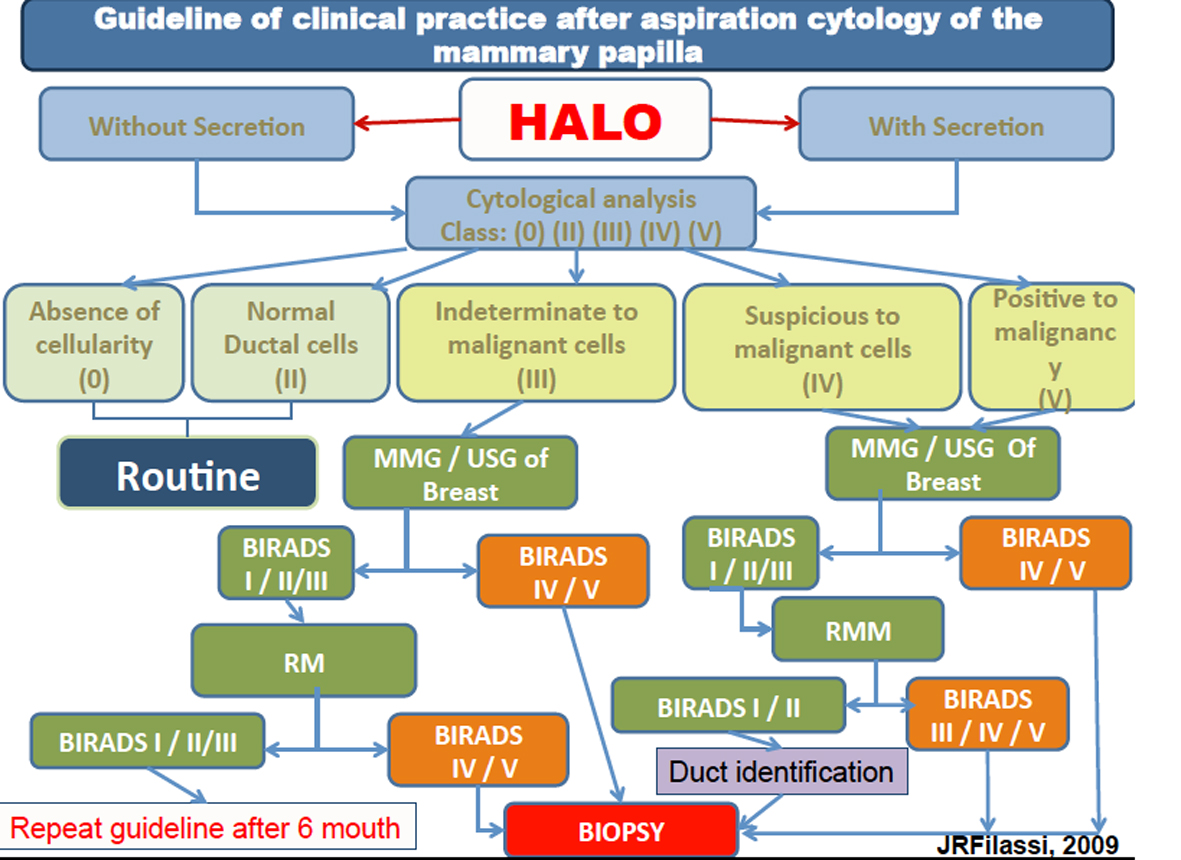
Tables
| Group I (159 women) | Group II (130 women) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 20 - 85 | 20 - 85 |
| Breast feeding | ||
| Yes | 112 (70.44%) | 112 (86.16%) |
| No | 47 (29.56%) | 18 (13.84%) |
| Family history of breast disease | ||
| Yes | 99 (62.27%) | 31 (23.84%) |
| No | 60 (37.73%) | 99 (76.16%) |
| Nipple discharge | ||
| Yes | 67 (42.14%) | 33 (25.39%) |
| No | 92 (57.86%) | 97 (74.61%) |
| History of breast disease | ||
| Yes | 5 (3.15%) | 31 (23.85%) |
| No | 154 (96.85%) | 99 (76.15%) |
| Method 1 | Method 2 (modified by Zonta & Velame) | |
|---|---|---|
| Preserved medium | Methanol 8% | SurePath ethanol-based medium |
| Technical procedure | 1 mL of sample fluid | 2 mL of sample fluid |
| Vortex 15 s/3,000 rpm | Vortex 15 s/3,000 rpm | |
| 10 min at 800 g | 10 min at 800 g | |
| Cells pellet | Cells pellet | |
| 1 mL of Tris buffer (Sigma) | 1 mL of Tris buffer (Sigma) | |
| 1 mL of homogeneous cells pellet | 1 mL of homogeneous cells pellet | |
| 10 m slyde fixing | 20 m slyde fixing |
| National Statistics and The National Health Service Breast Screening Programme (NHSBSP) | |
| Class 0 | Unsatisfactory material: absence of cells |
| Class II | Negative for malignancy |
| Class III | Indeterminate for malignancy |
| Class IV | Suspicious for malignancy |
| Class V | Positive for malignancy |
| Cellular changes | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| Unsatisfactory | 199 (65.0%) |
| Benign cells - class II | 104 (34.0%) |
| Atypical cells - class III | 3 (1.0%) |
| Total | 306 (100%) |
| Cellular changes | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| Unsatisfactory - class 0 | 127 (49.0%) |
| Benign cells - class II | 124 (48.0%) |
| Atypical cells - class III | 7 (3.0%) |
| Total | 258 (100%) |
| Women age (method 1) | Unsatisfactory (%) | Benign cells (%) | Atypical cells (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class 0 | Class II | Class III | |
| 20 - 25 | 5 (1.63%) | 3 (0.98%) | 0 (0%) |
| 26 - 35 | 10 (3.27%) | 8 (2.61%) | 0 (0%) |
| 36 - 45 | 49 (16.01%) | 12 (3.92%) | 0 (0%) |
| 46 - 55 | 85 (27.78%) | 61 (19.93%) | 1 (0.33%) |
| 56 - 65 | 41 (13.40%) | 13 (4.25%) | 1 (0.33%) |
| 66 - 75 | 8 (2.61%) | 4 (1.31%) | 1 (0.33%) |
| 76 - 85 | 1 (0.33%) | 3 (0.98%) | 0 (0%) |
| Total of samples | 199 (65.03%) | 104 (33.98%) | 3 (0.99%) |
| Women age (method 2) | Unsatisfactory (%) | Benign cells (%) | Atypical cells (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class 0 | Class II | Class III | |
| 20 - 25 | 6 (2.32%) | 4 (1.55%) | 0 (0%) |
| 26 - 35 | 15 (5.81%) | 14 (5.43%) | 1 (0.39%) |
| 36 - 45 | 27 (10.46%) | 32 (12.40%) | 3 (1.16%) |
| 46 - 55 | 45 (17.44%) | 37 (13.34%) | 2 (0.77%) |
| 56 - 65 | 13 (5.04%) | 25 (9.69%) | 0 (0%) |
| 66 - 75 | 12 (4.65%) | 6 (2.32%) | 0 (0%) |
| 76 - 85 | 9 (3.49%) | 6 (2.32%) | 1 (0.39%) |
| Total of samples | 127 (49.17%) | 124 (48.05%) | 7 (2.71%) |
| Total | 258 (100%) |