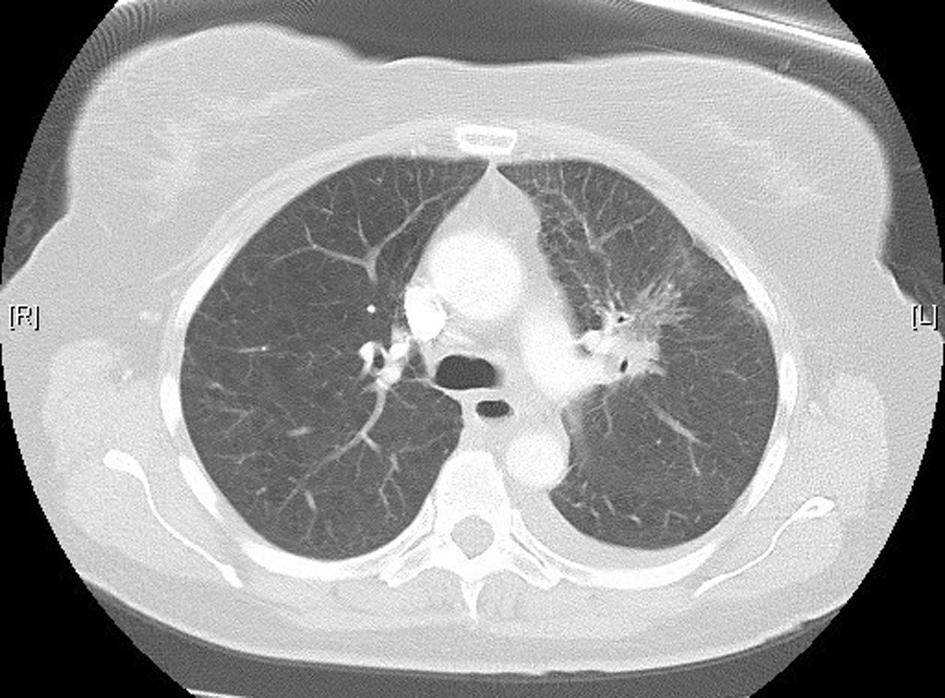
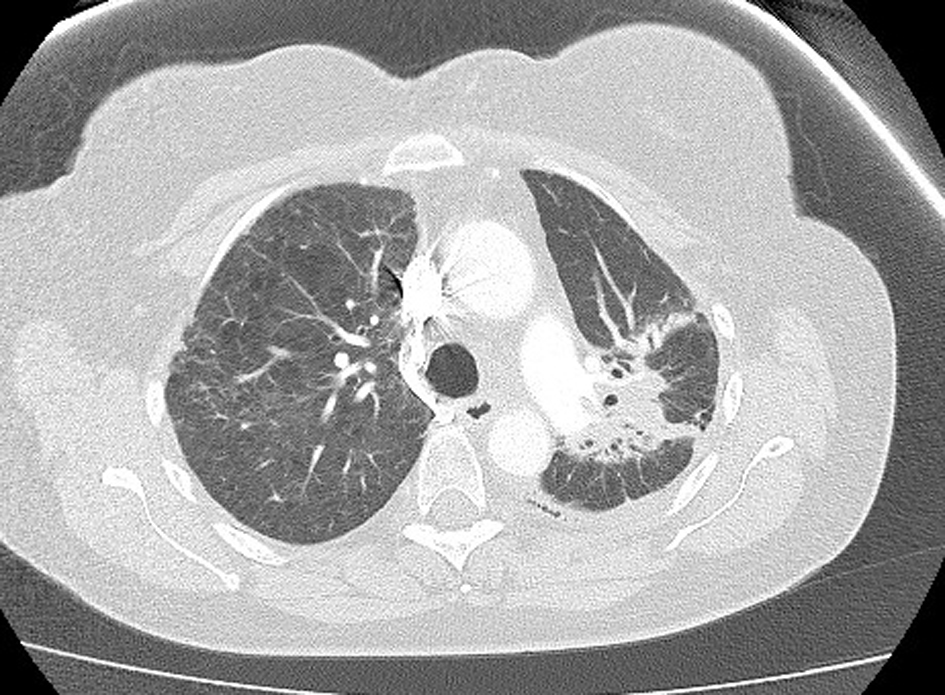
Figure 1. High-resolution lung computed tomography before pemetrexed administration.
| World Journal of Oncology, ISSN 1920-4531 print, 1920-454X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, World J Oncol and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.wjon.org |
Case Report
Volume 5, Number 5-6, December 2014, pages 232-236
Pemetrexed-Induced Interstitial Pneumonitis: A Case Study and Literature Review
Figures

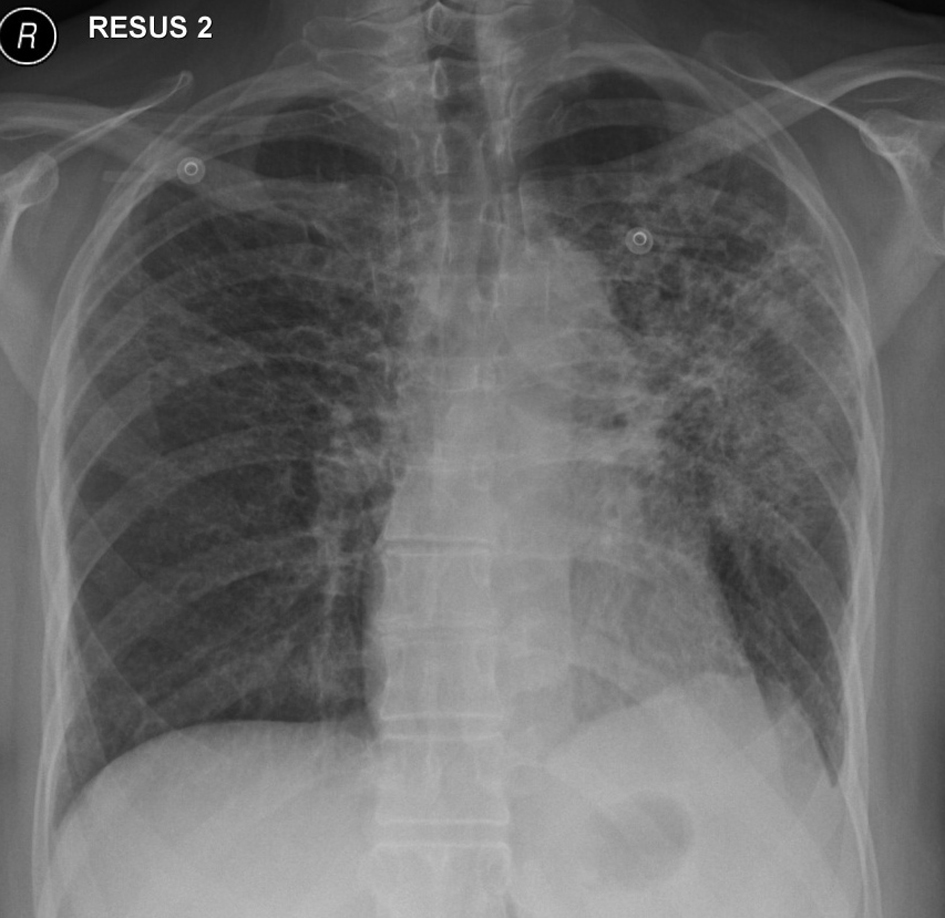
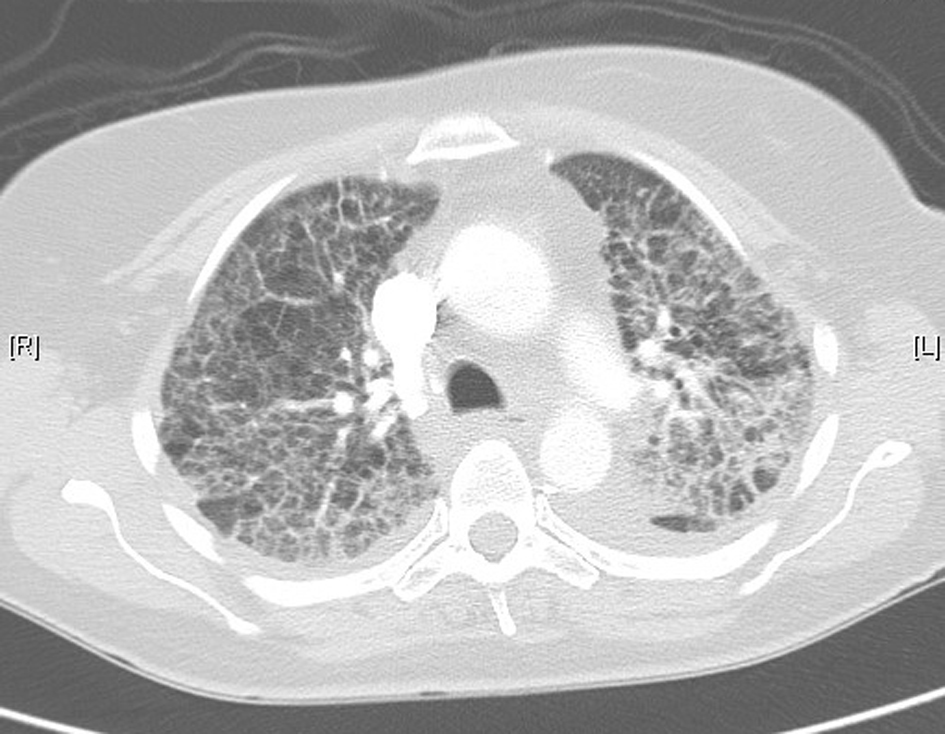
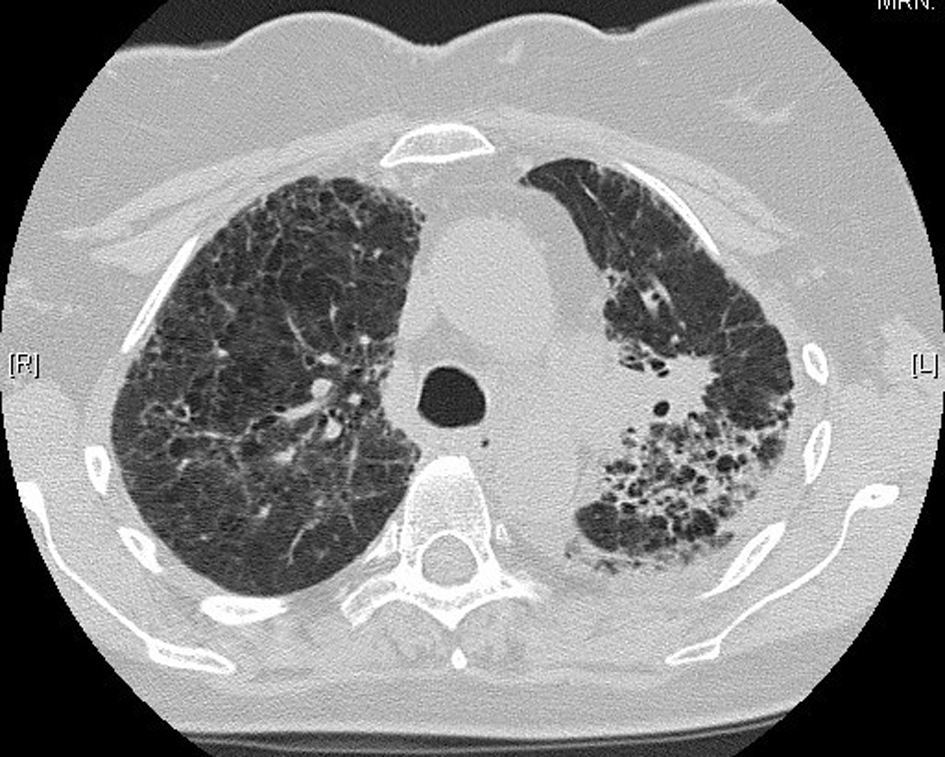
Table
| Case | Number of cycles | Time of symptom onset after last dose | Prior radiation | BAL | Biopsy confirmation | Rechallenged | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAL: Bronchoalveolar lavage; CT: computed tomography; (-): information not available from case report. | |||||||
| Loriot et al 2009 [10] | 5 | 3 days | No | Yes | No | No | Returned to pre-morbid status. Signs of pulmonary fibrosis on CT. |
| Kim et al 2010 [11] | 4 | “Shortly after” | No | No | Yes | No | “Slow improvement”. |
| Nagata et al 2010 [12] | 1 | 4 weeks | No | No | No | No | Died 3 weeks after symptom onset. |
| Nagata et al 2010 [12] | 1 | 3 weeks | No | No | No | No | Died 2 weeks after symptom onset. |
| Breuer and Nechushtan 2011 [13] | 4 | - | No | No | No | Yes | Pneumonitis recurred after rechallenge. Symptoms resolved in 2 weeks. |
| Hochstrasser et al 2012 [14] | 2 | 1 week | Yes | No | No | Yes | Pemetrexed was continued. Patient died 5 days after next dose. |
| Hochstrasser et al 2012 [14] | 2 | - | No | Yes | No | No | Improved rapidly; symptoms resolved. |
| Kim et al 2013 [15] | 1 | 3 weeks | No | Yes | Yes | No | Recovered; commenced erlotinib. |
| Waters et al 2013 | 2 | 13 days | Yes | No | No | No | Improved rapidly. |